The world is facing an "unrelenting march" of diabetes which now affects nearly one-in-11 people, the World Health Organization (WHO) says.
In a major report it warned cases had quadrupled from 108 million in 1980 to 422 million in 2014.
High blood sugar levels are a major killer - linked to 3.7 million deaths around the world each year, it says.
And officials said the numbers would continue to increase unless "drastic action" was taken.
The report lumps both type 1 and type 2 diabetes together, but the surge in cases is predominantly down to type 2 - the form closely linked to poor lifestyle.
As the world's waistlines have ballooned - with one-in-three people now overweight, so too has the number of diabetes cases.
How diabetes has taken its toll
422 million adults were living with diabetes in 2014 - that's 314 million more than there were in 1980
8.5% of adults worldwide has diabetes
1.5 million people died as a result of diabetes in 2012
2.2 million additional deaths were caused by higher-than-optimal blood glucose
43% of these 3.7m people died before they were 70 years old
Source: WHO
Dr Etienne Krug, the WHO official in charge of leading efforts against diabetes, told the BBC: "Diabetes is a silent disease, but it is on an unrelenting march that we need to stop.
"We can stop it, we know what needs to be done, but we cannot let it evolve like it does because it has a huge impact on people's health, on families and on society."
Failing to control levels of sugar in the blood has devastating health consequences increasing the risk of heart attacks, stroke, kidney failure, blindness, limb amputations and complications in pregnancy.
Diabetes itself is the eighth biggest killer in the world accounting for 1.5 million deaths each year.
But a further 2.2 million deaths are linked to high blood sugar levels.
Moving burden
In the 1980s the highest rates were found in affluent countries.
But, in a remarkable transformation, it is now low and middle income countries bearing the largest burden.
Dr Krug told the BBC News website: "That's where we see the steepest increase. Knowing that's where most of the population lives in the world, it does show numbers will continue to increase unless drastic action is taken."
The Middle East has seen the prevalence of diabetes soar from 5.9% of adults in 1980 to 13.7% in 2014.
Dr Slim Slama, a WHO specialist in region, told the BBC News website: "We are the region that has experienced the greatest rise in diabetes, moving 6 million to 43 million - it is a huge, huge increase.
"In Qatar or Kuwait we have more than 20% of the population with diabetes and when you look at subgroups - people beyond 45 or 60 years old - it's 30-40% and things are even more worrying."
Deadly diabetes in 'unrelenting march' - BBC News
Results 1 to 17 of 17
-
06-04-2016, 04:43 PM #1Thailand Expat
































- Join Date
- Aug 2013
- Last Online
- 01-07-2016 @ 05:52 AM
- Location
- Land of Laughs
- Posts
- 5,757
Deadly diabetes in 'unrelenting march'
-
09-04-2016, 09:52 AM #2god


- Join Date
- Nov 2006
- Last Online
- @
- Location
- Bangladesh
- Posts
- 28,210
Most recently diagnosed diabetics are generally stupid, carb addicted lazy fat c*nts, many with late onset (Type 2) diabetes, a manageable condition, IF the sufferers take control of themselves instead of being so self-indulgent.
The accompanying rise in Type 1 diabetes is also increasingly linked to obesity, as more kids are indulging in carbs/sugars and NO exercise than ever before due to a supposed rise in life-style standards/wealth.
The truth is we're digging our own graves with our teeth.
The accompanying rise in ADD/ADHD cases is also a result of over-weaning mums (particularly single mothers) pacifying their kids with sugary rewards.
Society's gone to hell, no self discipline left at all, just carrot and stick systems to keep all in order.
-
09-04-2016, 09:55 AM #3euston has flown































- Join Date
- Jun 2009
- Last Online
- 10-06-2016 @ 03:12 AM
- Posts
- 6,978
And so speaketh TD CSI.... peace be upon them
-
09-04-2016, 10:02 AM #4Thailand Expat


- Join Date
- Mar 2013
- Last Online
- @
- Location
- Last but who gives a shit.
- Posts
- 13,577
One in 13 Thais adults are diabetic.
WHO | Progress in diabetes control in ThailandIn the Thai langauge, diabetes is referred to as the “sweet urine disease”. In rural areas, villagers often first become aware that it is present because they notice ants gathering around their outdoor toilet.
http://www.worldlifeexpectancy.com/t...betes-mellitusLast edited by Pragmatic; 09-04-2016 at 10:11 AM.
-
09-04-2016, 12:14 PM #5
It is a convenient label for some people to avoid responsibility for their lifestyle. All it does, like other 'fashionable' afflictions, is create greater earnings for big pharma.
-
09-04-2016, 12:21 PM #6
One does not have to go to far to see a massive fat bastard farang sitting on a bar stool drinking piss and smoking cigs.
I mean it's gona kill ya innit.
I like to have a drink as well but I monitor my weight, put on a Kilo and I go off the piss for few days. Gota keep a handle on it.
Weight piles on easily when older and drinking piss is a major cause.
Plus go for a nice walk helps things.
I don't smoke thank fuk.
-
09-04-2016, 02:11 PM #7
The children now love luxury; they have bad manners, contempt for authority; they show disrespect for elders and love chatter in place of exercise. Children are now tyrants, not the servants of their households. They no longer rise when elders enter the room. They contradict their parents, chatter before company, gobble up dainties at the table, cross their legs, and tyrannize their teachers
Socrates (469–399 B.C.)
-
09-04-2016, 02:15 PM #8god


- Join Date
- Nov 2006
- Last Online
- @
- Location
- Bangladesh
- Posts
- 28,210
There's nothing new under the sun, only repeated, eh.
Humanity seems to take two steps forward and one step back in its progress.
I think it's called evolution.
-
09-04-2016, 02:16 PM #9god


- Join Date
- Nov 2006
- Last Online
- @
- Location
- Bangladesh
- Posts
- 28,210
-
09-04-2016, 02:25 PM #10
I blame much of this on lazy parents, particularly in Thailand where fast foods loaded with sugar have become more readily available. The endless sweet snacks given to children has caused a huge upswing in obesity over the past 5-10 years which predisposes them to diabetes. The same trend was seen in the west and is responsible for their upswing in diabetes as well.
Will Thailand change? I don't think so since they seem to listen much less to sound medical advice than westerners do. Better start buying Lilly stock now.
-
09-04-2016, 03:04 PM #11Perhaps westerners are just more gullible. If you don't have a medical fad label these days you are worthless.
 Originally Posted by rickschoppers
Originally Posted by rickschoppers
-
09-04-2016, 03:44 PM #12god


- Join Date
- Nov 2006
- Last Online
- @
- Location
- Bangladesh
- Posts
- 28,210
My sister's a bit like that, broadcasts her infirmities on facebook.
-
10-04-2016, 07:24 PM #13Tits oot?
 Originally Posted by ENT
Originally Posted by ENT
-
10-04-2016, 08:09 PM #14god


- Join Date
- Nov 2006
- Last Online
- @
- Location
- Bangladesh
- Posts
- 28,210
Nearly, but a bit too old and fat for that, the awl' slapper.

-
10-04-2016, 09:35 PM #15Member
















- Join Date
- Sep 2013
- Last Online
- 11-06-2017 @ 09:47 PM
- Posts
- 265
-
11-04-2016, 12:08 PM #16
What? There are plenty of fake or exaggerated diseases used by malingerers or hypochondriacs, but diabetes is not one of them. Blood sugar can be easily measured and charted.
Also, look at the supply of available food; if you discard everything the "experts" say can be harmful, there's not much left to choose from.
-
11-04-2016, 12:20 PM #17Yes, and those in search of a better class of illness will use the popularity of diabetes to add weight to their facebook profile.
 Originally Posted by BobR
Originally Posted by BobR
Just ask yourself who produces and profits from the test kits? Those who automatically assume a high blood sugar count entitles them to a fad label can manipulate the test anyway. Originally Posted by BobR
Originally Posted by BobR
Thread Information
Users Browsing this Thread
There are currently 1 users browsing this thread. (0 members and 1 guests)


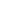
 Reply With Quote
Reply With Quote
