Wind developers bid $93M for mid-Atlantica — blowing off Trump 2.0 threat
The Biden administration notched a much-needed win on Wednesday in its bid to bolster the offshore wind power industry, despite the industry’s recent setbacks and the threat of former President Donald Trump’s return.
An Interior Department auction to lease federal waters for wind projects off the coasts of Delaware, Maryland and Virginia drew nearly $93 million in bids — an amount that appeared to quell nerves about the industry’s ability to withstand its political and economic headwinds.
The U.S. offshore wind industry plays a central role in President Joe Biden’s targets to cut carbon emissions from the power sector and stave off the worst effects of climate change. But the nascent industry has been plagued by rising costs, supply chain constraints, worrisome accidents and the risk that Trump, who has spent years attacking wind power, could undermine its progress.
“Despite the electoral uncertainty in the future, these are strong signals of confidence and continued interest in this market,” said Sam Salustro, senior vice president of policy for the Oceantic Network, an offshore wind industry group.
The $93 million is far less than the massive $4.4 billion that the Interior Department’s Bureau of Ocean Energy Management had received in a 2022 auction for the prime lease locations near New York and New Jersey. But that price hasn’t paid off for some of the developers, whose tentative agreements with New York were scrapped earlier this year. Others have secured contracts with New Jersey and are moving ahead.
But it was far more successful than auctions in the Gulf of Mexico. BOEM last month canceled a sale there due to lack of interest, and an auction in 2023 drew less than $6 million for a portion of the leases on offer.
The Biden administration set a goal to deploy 30 gigawatts of offshore wind energy capacity by 2030 — a target it is widely expected to miss. But the administration has remained bullish, approving nine commercial scale offshore wind projects under Biden and announcing plans to hold up to 12 offshore wind lease sales over the next five years.
The lease areas in Wednesday’s auction could generate as much as 6.3 gigawatts of power — or enough for up to 2.2 million homes.
While Vice President Kamala Harris is expected to carry Biden’s mantle on offshore wind, Trump has been vocally hostile to it, prompting concern that he could derail Democrats’ plans.
Trump has already pledged to sign an executive order “on Day One” targeting the offshore wind industry if he is elected to a second term.
Trump’s disdain for wind power stretches back to his fight against an offshore development in Scotland that he contended in legal challenges would spoil the views from a golf course he owns nearby. The U.K. Supreme Court rejected his claims in 2015, but the GOP presidential nominee has kept up his attacks on wind power, falsely claiming wind turbines don’t work, destroy property values, cause cancer and kill whales.
Even without Trump’s opposition, the offshore wind sector in the United States has struggled to get its footing, with developers canceling major planned wind farms off the coasts of New Jersey last year. The pandemic squeezed supply chains, driving up prices, and inflation made the contracts that wind developers signed to deliver electricity untenable.
Last month, a wind turbine at the massive Vineyard Wind development off Massachusetts saw a blade snap, sending shards into the waters and prompting the brief closure of beaches of Nantucket Island. The event has emerged as fodder for offshore wind opponents and left the local community with major questions.
Biden’s 2022 climate law, the Inflation Reduction Act, delivered new federal support to help the industry, but experts said Wednesday’s robust auction results owed just as much thanks to the states where the new developments would be sited.
Tim Fox, vice president at advisory firm ClearView Energy Partners, said Wednesday’s auction results “reinforce” the importance of state-led offshore wind actions and could suggest private developers may be looking further down the road than the next four years.
“This bidding could suggest that some project developers view the potential risks associated with a return on the Trump administration as overdone,” Fox said before Wednesday’s results — adding that it could also reflect the recent momentum of Harris’ presidential campaign.
The Central Atlantic lease sale comprised two areas of roughly 277,000 acres off the coasts of Delaware, Maryland and Virginia. It resulted in two provisional winners and $92.65 million in winning bids.
That drew a welcome response from the White House.
“Today’s lease sale reflects the forward momentum we are seeing to power millions of American homes with clean energy and create good-paying, climate jobs,” Ali Zaidi, Biden’s top climate adviser, said in a statement.
Equinor Wind US, a unit of Norway’s state-owned energy company, provisionally won acreage about 26 nautical miles from Delaware Bay with a bid of roughly $75 million, and a unit of Dominion Energy provisionally won acreage 35 nautical miles from the entrance of Chesapeake Bay with a winning bid just under $17.7 million.
Pĺl Eitrheim, executive vice president of Equinor Renewables, said the announcement “underscores” Equinor’s commitment to delivering value through renewable energy projects. “This is a long-term option with first power post 2035,” Eitrheim said in a statement.
Seventeen companies had initially qualified to participate in the sale and six companies ultimately participated in the auction.
Those bids are also buoyed by state-level targets. Maryland is targeting 8.5 gigawatts of power by 2031 and Virginia set a 5.2-gigawatt target by the mid 2030s. Delaware’s legislature passed a bill awaiting the governor’s signature that would enable an offshore wind solicitation to procure up to 1.2 gigawatts.
The auction — the first for the region in a decade — “continues movement in the right direction” for U.S. offshore wind deployment and in the mid-Atlantic, said Sarah Giltz, the director of offshore wind for the labor-environmental advocacy group called the BlueGreen Alliance, in a statement Wednesday.
One of the areas auctioned Wednesday, offshore Delaware and Maryland, consists of roughly 101,400 acres, while the area off Virginia consists of 176,500 acres.
The results Wednesday equate to roughly $100 per acre off the coast of Virginia, while the other area earned roughly $740 per acre. That falls short of the high-level bids seen in earlier auctions under Biden — although the economics and market dynamics of the industry have changed significantly since then.
“The lead-up to those other leases was a time of really unfettered optimism,” said Salustro. Since then, he noted, there’s been market corrections both locally and globally, making it largely “unfair” to compare earlier prices with pricing today.
A lease sale for the New York waters in 2022 — the first under Biden — raked in a record $4.4 billion, while a West Coast sale saw $757 million and sites off the Carolinas, which are near Wednesday’s areas, garnered more than $300 million.
Still, the bidding levels Wednesday exceeded last year’s first-ever Gulf of Mexico offshore wind lease sale, which received lackluster interest, with one lease area of the three that were offered receiving a winning bid of $5.6 million.
“I would argue there’s still momentum for the industry,” ClearView’s Fox said. “It’s just more cautious after the material setbacks witnessed in recent years and the continuation of the macro-economic pressures.”
Erik Milito, the president of the National Ocean Industries Association, which represents both the offshore oil and gas and wind industries, said the lease area in Maryland and Delaware “saw a substantial increase in bid amounts, multiplying several times over compared to a decade ago,” while the lease area offshore Virginia fetched significantly higher prices than similar leases.
“However, Washington needs to do more to maintain this momentum,” he said in an emailed response. He noted that this is the first year without a federal offshore oil and gas lease sale since 1958 and that after December, the Interior Department cannot hold any more offshore wind lease sales until another offshore oil and gas sale is held — thanks to a provision in Democrats’ climate law
“The current leasing reality is begging for a Congressional fix to provide much-needed regulatory certainty and normalcy for both offshore oil and gas and wind lease sales,” he said.
Results 751 to 775 of 801
Thread: Fossil Fuel Alternatives
-
15-08-2024, 08:06 AM #751Keep your friends close and your enemies closer.
-
17-08-2024, 01:02 PM #752
United Downs will soon deliver UKÂ’s first geothermal electricity as generation turbine is installed

The turbine that converts geothermal steam into electricity has been successfully installed at the UKĂ‚Â’s first geothermal power plant.
It is powered by fluid heated by geothermal brine several miles below the Earth’s surface. This rotates the turbine which is connected to a generator that converts kinetic energy into electricity.
Site operator – Geothermal Engineering Limited (GEL) – predicts United Downs will deliver 2MWe of baseload electricity once operational, plus additional zero carbon heat for local housing, hospitals and schools. The site also has the potential to fulfil a significant portion of the UK’s lithium demand. Tests at United Downs have shown that geothermal fluid within the wells has one of the highest concentrations of lithium in Europe at 340 parts per million (ppm). This sustainably produced lithium could be used to support the growing EV industry as we transition to net zero.
___________
Green vision for old Chapelcross nuclear plant site unveiled
A masterplan for turning an old nuclear plant site into a "green energy hub" has been unveiled.
The aim is to help the land at Chapelcross near Annan bring high value jobs to the area and transform the local economy.
The project is backed by more than Ă‚ÂŁ15m from the Scottish and UK governments.
It includes hydrogen production and storage as well as energy and enterprise campuses.
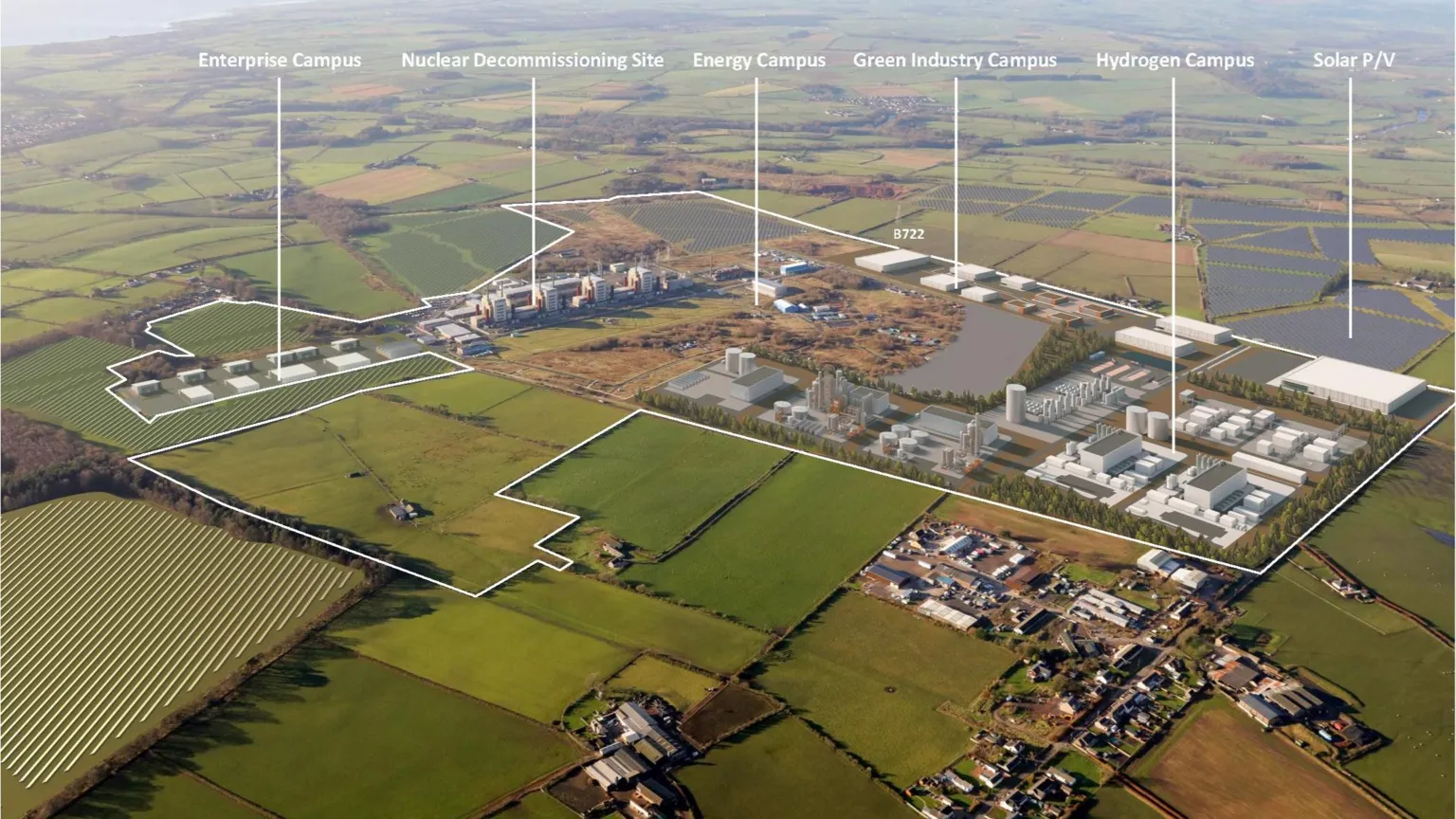
The Chapelcross site ceased generating electricity in 2004 and its cooling towers came down a few years later.
It covers an area of more than 210 hectares (520 acres).
Dumfries and Galloway Council leader Gail Macgregor said the masterplan set out a "clear vision" for delivering jobs for the region.
She said they were working with the Nuclear Decommissioning Authority and South of Scotland Enterprise to make the site a "powerful force for change".
Plans are also in development for a battery energy storage facilily on land nearby.
___________
Sun Line Transit Agency Receives $500,000 for Renewable Energy Projects
Sun Line Transit Agency was awarded $500,000 in funding from Congressman Raul Ruiz and Senator Alex Padilla to support its energy independence initiatives. The funding will be used to develop a solar microgrid in Thousand Palms, which will collect, store, and distribute solar energy to fuel hydrogen-powered buses, helping to reduce emissions and improve air quality in the Coachella Valley. The agency also aims to enhance its bus system and combat diseases like asthma and COPD, prevalent due to high pollution levels in the area.
____________
Barbados News - Senator Lisa Cummins Leads First Battery Energy Storage Initiative Barbados Real Estate
Barbados is set to launch its inaugural Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) project, a significant step towards enhancing the country’s renewable energy infrastructure. This initiative aims to bolster the electricity grid and facilitate the connection of previously stalled solar photovoltaic (PV) systems.
The Ministry of Energy and Business is spearheading a three-day Procurement Design Workshop, bringing together stakeholders from organizations such as Renewables for All, the Global Energy Alliance for People and Planet, the Inter-American Development Bank, Deloitte, the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, and the International Finance Corporation. The primary goal of the workshop is to finalize the procurement details for the BESS project.

Barbados is poised to address its energy storage needs with the BESS project, providing a reliable solution to support its growing renewable energy sector. Minister of Energy and Business, Senator Lisa Cummins, highlighted the project’s significance at the Warrens Office Complex, stating, “This has been an urgent priority for our Government. The partners have spent a lot of time collaborating with my team because they understand how critical this is. The discussions over the next few days will help finalize the process to bring battery energy storage systems into the country. This is a watershed moment that many have been waiting for.”
The consortium of experts supporting Barbados began their efforts in early 2024, conducting a grid characterization study that informed the project’s design. Their work, including market sounding sessions, aims to develop a cost-effective and competitive BESS tailored to Barbados’ needs. Local agencies involved in the collaboration include the Fair Trading Commission, the Central Bank, Government Procurement, GEED, and the Bankers’ Association.
In addition to the BESS project, Barbados is planning a 50MW photovoltaic plant combined with 128MWh of long-term green hydrogen storage and batteries in St. Philip. This facility aims to replace heavy fuel oil and kerosene consumption, aligning with the country’s goal of achieving 100% renewable energy by 2030.
As the BESS project approaches completion, Barbadians awaiting grid connections can anticipate accessing solar energy, allowing new projects to move forward. The successful implementation of these initiatives underscores Barbados’ commitment to sustainable energy solutions and its role as a regional leader in renewable energy adoption.
__________
ADB Invests $100 Million in Fourth Partner Energy to Support Decarbonization of IndiaÂ’s Commercial and Industrial Sector

The Asian Development Bank (ADB) has signed a $100 million equity investment with leading independent power producer Fourth Partner Energy Private Limited to advance the decarbonization of India’s commercial and industrial sector through utility-scale solar, solar-wind hybrid and rooftop solar power projects and to provide cost-effective clean energy directly to users.
The financing includes $70 million from ADB’s ordinary capital resources and $30 million from Leading Asia’s Private Infrastructure Fund 2 (LEAP 2), administered by ADB. Deutsche Investitions- und Entwicklungsgesellschaft (DEG) and the International Finance Corporation (IFC) are joint investors.
"Providing commercial and industrial users in India with access to clean and renewable energy will foster growth of the sector while helping to achieve net-zero emissions," said ADB Director General for Private Sector Operations Suzanne Gaboury. "ADB's investment will support the clean energy transition by encouraging domestic and international lenders to engage with independent power producers in this sector."
“Our investors and lenders keep coming back as financiers because FPEL prioritizes commercial viability and robust returns, while focusing on scaling the business,” said Fourth Partner Energy Co-founder & Executive Director Vivek Subramanian. “We welcome IFC, ADB and DEG as new partners to join our existing high-quality equity investor base comprising of Norfund and TPG. Fourth Partner Energy is now poised to transform the region’s clean energy landscape and assist more businesses in reaching their RE100 goals in a just and equitable manner.”
__________
Global EV competition intensifies as China challenges EU tariffs
China is challenging the European Union's plan to impose tariffs on Chinese electric vehicles.
Why it matters: The move further escalates global tension over protectionist policies related to EVs.
The big picture: The U.S. and the EU have accused China of unfairly subsidizing its EV market.
- The Biden administration is imposing 100% tariffs on Chinese EVs to the U.S.
- China, for its part, has already filed a complaint with the WTO alleging that EV credits in the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act violate trade rules.
The latest: China filed an appeal with the World Trade Organization Friday, saying the EU tariffs violate WTO rules and hurt the global fight against climate change, state media reported.
- The EU recently announced plans to impose a 37.6% levy on Chinese EVs, which are flooding into the market and posing a competitive threat to European automakers.
The EU signaled Friday that it will move forward with its tariffs, which would go into effect in November.
- "The Commission is confident of the WTO-compatibility of its investigation and provisional measures," a Commission spokesperson told Reuters.
Reality check: Tariffs have little chance of masking the fact that Chinese automakers have a tremendous cost advantage over the rest of the global auto industry on EVs.
- "Think of the new European tariffs on Chinese cars like a glancing blow thrown by a fading heavyweight fighter, one that will not stop China's advance," Dunne Insights analyst and China auto expert Michael Dunne wrote in June.
- "The reality is that the Chinese are already woven into the fabric of Europe's car markets—and often in partnership with the Europeans themselves."
Meanwhile, Friday's move could have broader ripples.
What we're watching: The tit-for-tat is part of what "some analysts fear could develop into an economically harmful trade war with the EU," with China already investigating exports of French cognac and European pork, the AP reported.
-
24-08-2024, 12:00 PM #753
Solar Capacity Surges Tenfold in a Decade, Wind Energy Doubles
Washington DC – A review by the SUN DAY Campaign of mid-year data just released by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) reveals that the mix of renewable energy sources (i.e., biomass, geothermal, hydropower, solar, wind) is now 30% of total U.S. electrical generating capacity. Moreover, June was the tenth month in a row in which solar was the largest source of new capacity putting it on track to become the nation’s second-largest source of capacity – behind only natural gas – within three years.
Renewables were 99% of new generating capacity in June and 91% in 1st half of 2024:
In its latest monthly “Energy Infrastructure Update” (with data through June 30, 2024), FERC says 37 “units” of solar totaling 2,192 megawatts (MW) were placed into service in June along with one unit of hydropower (34-MW). Combined they accounted for 98.9% of all new generating capacity added during the month. Natural gas and oil provided the balance: 20-MW and 5-MW respectively. [1]
During the first half of 2024, solar and wind added 13,072-MW and 2,129-MW respectively. Combined with 212-MW of hydropower and 3-MW of biomass, renewables were 91.2% of capacity added. The balance consisted of the 1,100 Vogtle-4 nuclear reactor in Georgia plus 369-MW of gas, 11-MW of oil, and 3-MW of “other.”
Solar was 97% of new capacity in June and 77% during the first six months of 2024:
The new solar capacity added from January through June this year was more than double the solar capacity (6,446-MW) added during the same period last year. Solar accounted for 77.4% of all new generation placed into service in the first half of 2024.
New wind capacity YTD accounted for most of the balance – 12.6% but that was slightly less than that added during the same time frame in 2023 (2,761-MW).
In June alone, solar comprised 97.4% of all new capacity added, followed by hydropower (1.5%).
Solar has now been the largest source of new generating capacity for ten months straight: September 2023 – June 2024. For seven of those ten months, wind took second place.
_______
MIT engineersÂ’ new theory could improve the design and operation of wind power plant
The first comprehensive model of rotor aerodynamics could improve the way wind turbine blades and wind farms are designed and how wind turbines are controlled.
The blades of propellers and wind turbines are designed based on aerodynamics principles that were first described mathematically more than a century ago. But engineers have long realized that these formulas don’t work in every situation. To compensate, they have added ad hoc “correction factors” based on empirical observations.
Now, for the first time, engineers at MIT have developed a comprehensive, physics-based model that accurately represents the airflow around rotors even under extreme conditions, such as when the blades are operating at high forces and speeds, or are angled in certain directions. The model could improve the way rotors themselves are designed, but also the way wind farms are laid out and operated. The new findings are described today in the journal Nature Communications, in an open-access paper by MIT postdoc Jaime Liew, doctoral student Kirby Heck, and Michael Howland, the Esther and Harold E. Edgerton Assistant Professor of Civil and Environmental Engineering.
“We’ve developed a new theory for the aerodynamics of rotors,” Howland says. This theory can be used to determine the forces, flow velocities, and power of a rotor, whether that rotor is extracting energy from the airflow, as in a wind turbine, or applying energy to the flow, as in a ship or airplane propeller. “The theory works in both directions,” he says.
Because the new understanding is a fundamental mathematical model, some of its implications could potentially be applied right away. For example, operators of wind farms must constantly adjust a variety of parameters, including the orientation of each turbine as well as its rotation speed and the angle of its blades, in order to maximize power output while maintaining safety margins. The new model can provide a simple, speedy way of optimizing those factors in real time.
“This is what we’re so excited about, is that it has immediate and direct potential for impact across the value chain of wind power,” Howland says.
________
ChinaÂ’s New Renewable Energy Output Rivals UKÂ’s Total Electricity Generation

China has achieved a significant milestone in renewable energy production, matching the UK’s total electricity output from all sources with its new clean energy generation in the first half of this year. The rapid expansion in wind and solar power capacities underscores China’s position as the leading nation in renewable energy, according to the Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air (CREA). This development is a key component in the global strategy to mitigate Climate change.
Despite its status as the world’s largest emitter of greenhouse gases, China has made remarkable strides in reducing reliance on fossil fuels. The nation witnessed a 5% decline in coal and gas electricity generation in July compared to the previous year. Renewable energy, particularly solar and wind, has not only supplemented but in some areas surpassed coal-fired electricity. By 2026, it is projected that solar power alone will exceed coal as China’s main energy source, boasting a capacity of over 1.38 terawatts — 150GW more than coal.
________
Ola Launches Electric Bike Roadster: All You Need To Know
-
31-08-2024, 05:10 PM #754
Norway's sovereign wealth fund commits $1 bln to renewable energy fund
Norway's sovereign wealth fund said on Monday it will commit 900 million euros ($1.01 billion) to the latest renewable energy fund of Copenhagen Infrastructure Partners (CIP), APA reports citing Reuters.
Norges Bank Investment Management said in a statement it had agreed to commit the sum to CIP's fifth flagship fund CI V, which will focus on investing in offshore and onshore wind, solar farms, grid and distribution, as well as storage.
________
Prime Minister Announces Approval of Two Major Renewable Energy Projects
Prime Minister Mostafa Madbouly has announced that the Cabinet has approved two significant renewable energy projects involving direct foreign investment. These projects are a key part of EgyptÂ’s strategy to bolster its renewable energy capacity.
The government aims to add over 4 gigawatts of renewable energy to the national grid next year, with a target of increasing this capacity to 28 gigawatts within the next five to seven years. These initiatives are critical to addressing the countryÂ’s ongoing energy challenges.
Prime Minister Madbouly shared this update during his weekly press conference following the Cabinet meeting.
He also highlighted two notable events in the energy sector this week. The first was the launch of EgyptÂ’s first voluntary carbon market by the Financial Regulatory Authority, a significant step in promoting green energy. The second was the formal announcement of the national low-carbon hydrogen strategy, demonstrating the governmentÂ’s strong commitment to advancing sustainable energy initiatives.
_________
In boosting clean energy in Minnesota, Walz lays foundation for climate influence if Harris wins
When Minnesota Gov. Tim Walz strolled onstage to welcome a conference of clean power advocates to Minneapolis in May, he was quick to note that his state is now getting a little over half of its power from renewables. In the next breath, Walz said Minnesota would never get to 100% — a goal he helped set — without changing what he called “outdated” permitting laws.
“There are things we are doing that are too cumbersome, they don’t fit where we’re at, they add costs, and they make it more prohibitive to get where we need to go," Walz told the industry group American Clean Power.
A few weeks later, he signed legislation to speed things up. Developers no longer have to demonstrate that a clean energy project — that is, solar and wind, storage and transmission projects — is needed as part of Minnesota's energy system. And they no longer have to study alternative sites and transmission line routes — a requirement that had effectively doubled the possible opponents for a project.
Walz's effort to resolve a major obstacle to the clean energy transition nationwide is getting new attention since he was tapped as Kamala Harris' running mate. His experience enacting such laws in Minnesota could position him as a leader on climate issues if Harris wins in November.
“If Gov. Walz becomes our VP, I hope he could help bring some of this thinking to the federal level,” said Amelia Vohs, climate program director at the Minnesota Center for Environmental Advocacy, a group that was involved in helping produce the permitting reforms. “It would make an incredible difference in the nation’s progress on climate."
https://abcnews.go.com/US/wireStory/...mate-113132812
_________
SD Leader In Wind Energy Production Last Year

(Sioux Falls, SD) — South Dakota is a leader in wind energy production, according to a new report. The Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy says the state was second in the nation in wind energy generated last year. The report also revealed wind energy was more than half out off all the energy South Dakota generated in 2023. But, South Dakotans only consumed 19 percent of it compared to other methods. The state has an installed capacity of over 36-hundred mega-watts.
https://dakotanewsnetwork.com/south-...ion-last-year/
__________
California Launches $500M Program to Speed Transition to Zero-Emission School Buses
California is launching a new statewide funding program that will put 1,000 new, zero-emission school buses on the road, furthering the stateÂ’s lead in having the largest number of clean buses in the nation.
“California is showing the nation and the world how to move from ambition to action,” says Gov. Gavin Newsom. “This is yet another record state investment that puts the health of our kids and communities first — replacing 1,000 older polluting school buses with clean buses.”
The program will distribute $500 million to school districts and other educational entities to replace aging school buses with zero-emission vehicles and purchase needed infrastructure. The Zero-Emissions School Bus and Infrastructure (ZESBI) program is accepting funding applications through Sept. 30.
As California continues to lead in the deployment of zero-emission vehicles and in building the necessary infrastructure, the focus on school buses targets a sector where the switch to cleaner technology will lead to better public health outcomes for schoolchildren and the communities where they live.
The program is a collaboration between the California Air Resources Board (CARB) and the California Energy Commission (CEC), and is administered by CALSTART, a transportation nonprofit.
“Children are especially vulnerable to the impacts of diesel pollution, so transitioning to clean school buses is key to protecting our kids’ health while getting them to school safely,” says CARB Chair Liane Randolph. “The investments that California is making in zero-emission school bus technology will pay off in cleaner air, modernized fleets for our schools and healthier communities.”
https://ngtnews.com/california-launc...n-school-buses
________
Biden administration releases plan to expand US West solar development
The Bureau of Land Management (BLM) is considering making 31 million acres of public lands across the western U.S. available for potential solar energy development, according to a proposal published on Thursday.
The Western Solar Plan, which would significantly revise existing 2012 guidelines, would seek to bring such projects to 11 states — bringing development closer to transmission lines or previously disturbed lands, per the proposal.
“The updated Western Solar Plan is a responsible, pragmatic strategy for developing solar energy on our nation’s public lands that supports national clean energy goals and long-term national energy security,” BLM Director Tracy Stone-Manning said in a statement.
Chief among the changes was the identification of five new states beyond the original six as prime areas for solar energy. In addition to Arizona, California, Colorado, Nevada, New Mexico and Utah, the updated version includes Idaho, Montana, Oregon, Washington and Wyoming.
After examining six different alternatives, the BLM landed on the option that would enable potential solar development on 31 million out of 162 million available acres of public lands in the region, according to the proposal.
Of those 31 million acres, the lands would be available for use only if they are within 15 miles of an existing or planned high-voltage transmission line or if they have been categorized as “previously disturbed,” the document states.
https://thehill.com/policy/energy-en...r-development/
________
Lego plans to make half the plastic in bricks from renewable materials by 2026
Lego plans to make half the plastic in its bricks from renewable or recycled material rather than fossil fuels by 2026, in its latest effort to ensure its toys are more environmentally friendly.
The Danish company last year ditched efforts to make bricks entirely from recycled bottles because of cost and production issues. At the moment, 22% of the material in its colourful bricks is not made from fossil fuels.
In the long term, Lego plans to switch entirely to renewable and recycled plastic by 2032, in a green push that has resulted in the company testing more than 600 alternative materials.
The toymaker hopes gradually to bring down the amount of oil-based plastic it uses by paying up to 70% more for certified renewable resin, the raw plastic used to manufacture the bricks, in an attempt to encourage manufacturers to increase production.
LegoÂ’s plastic producers are replacing virgin fossil fuels with alternatives such as cooking oil or food industry waste fat as well as recycled materials but costs can be two or three times higher because the market is still developing.
Niels Christiansen, the chief executive of Lego, said the shift towards more sustainable materials meant a significant increase in the cost of producing its bricks.
Last year, the group pledged to triple spending on sustainability to 3bn Danish kroner (ÂŁ340m) a year by 2025, while promising not to pass on higher costs to consumers.
“So far we have decided that we will bear the burden of it, and [the extra cost] comes out of our bottom line. We are not sure consumers are very willing to pay,” Christiansen told the Guardian.
He said Lego was making the investment to “try to push the industry to develop” and “shift the supply chain” by increasing demand and he said it was hoped this would eventually lead to the development of new or cheaper materials that would help Lego meet its 2032 target.
https://www.theguardian.com/lifeands...erials-by-2026
-
06-09-2024, 04:34 PM #755
First hydrogen solar panel destroys industry in China and Japan: It's white and 1000 times more powerful
China is terrified of the first hydrogen solar panel: It’s 1000 times more powerful than expected
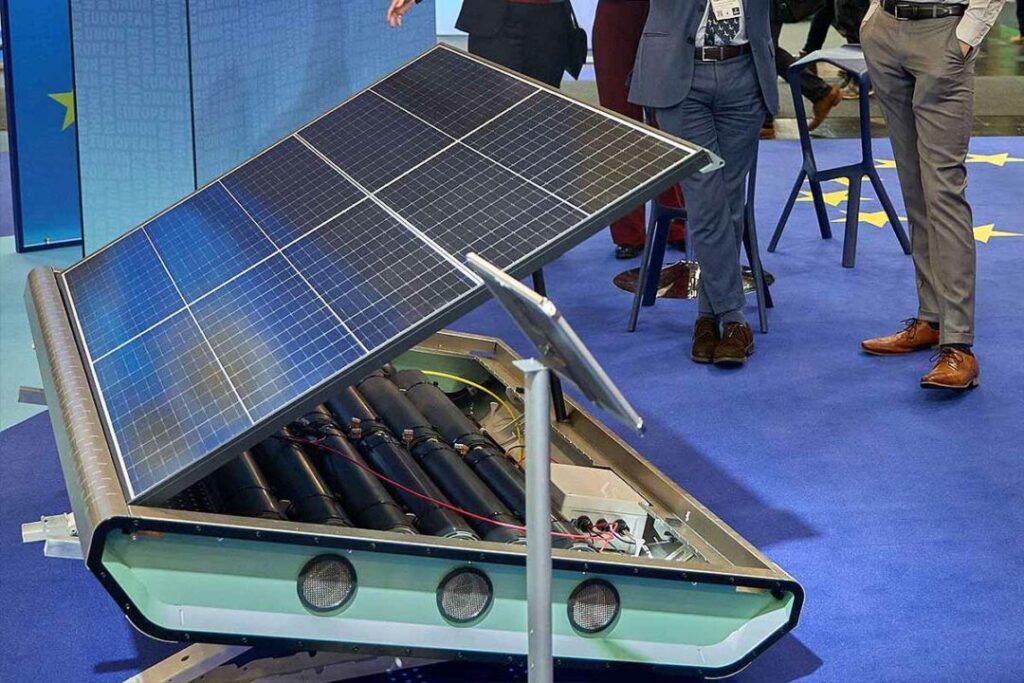

The University of Leuven in Belgium has worked on the Solhyd project, which is an exceptionally innovative idea for the solar panels to directly produce hydrogen from the sun and moisture in the air. This approach to hydrogen production has attracted the interest of the public and investors, thus placing Solhyd at a vantage point for becoming a game changer in the renewable energy industry.
The Solhyd hydrogen panel functions on a mechanism that makes it different from the normal solar panel and the electrolyzers. Broadly speaking, it integrates a regular PV panel with another specially designed layer, which generates hydrogen. The process starts with the adsorption of water vapor from the moist air, something the material excels at, especially during humidity.
This provides water vapor, which is then stored within the panel, absorbs it to provide the coil, and then directs some gaseous endothermally into the panel. That is, in sunlight, the panel’s photoelectrochemical cell decomposes the stored water vapor into hydrogen and oxygen gases.
This solar panel is so futuristic, it “ignores” sunlight: That’s how it works with the air
One of the significant components of this system is the membrane, which has the unique utility of collecting and focusing water vapor into the conversion cell. One of the patented techniques that differentiates the Solhyd approach is this membrane technology. The electricity from the top layer of the solar panel is used to turn the catalysts, which in turn break down the extracted air and water molecules.
This process happens independently of liquid water as well as not being tied to the power grid, making it a stand-alone system for hydrogen generation. To put the Solhyd panel’s performance into perspective, here are some key figures:
- One single module can generate about 6 kg of hydrogen per year in the northwestern European climate.
- For this type of module, the production may go up to twelve kilograms per module per year, especially in sunny areas.
- If equated to a roof installation that is half as large and has 20 hydrogen panels, then per year, the pant may generate 120 kg to 240 kg of hydrogen, which equates to about 4 MWh to 8 MWH of hydrogen energy.
- The panels function with a peak efficacy of 15%, for real-world efficiency, the aim is at 12% and above.
__________
Swedish geothermal developer Baseload Capital has announced the closing of its €53m Series B round of financing.
The Series B round was led by an investment from infrastructure fund ENGF, whose main investor is Ingka Investments.
Other shareholders participating in this round include energy technology company Baker Hughes – whose investment was announced in 2023 – Nefco, Breakthrough Energy Ventures, and Gullspĺng Invest.
Baseload Capital aims to address under-utilised resources and building a global collaborative portfolio of geothermal projects to scale the entire industry.
Funds will be used to commercialise the company’s current portfolio of projects.
Baseload Capital aims to unlock largely unexploited global geothermal potential, estimated at 200GWe and 5000GWth with existing technology.
Installed global capacity today is 16.3GWe and 173GWth.
According to the US Department of Energy, geothermal resources leveraged by technologies from the oil and gas industry could provide 90GW-300GW of clean firm capacity by 2050 in the US alone.
While the geothermal industry drills about 800 wells a year, it lags far behind the oil and gas industry that drills about 60,000-70,000 annually.
Baseload Capital and its Baseload Power subsidiaries operate in mature geothermal markets like Iceland, the US, and Japan, as well as in emerging markets like Taiwan.
In the latter, it is taking an active part in shaping the first-ever geothermal policies.
Baseload Capital chief executive Alexander Helling said: "The trust these renowned partners place in us is a testament both to what we at Baseload can achieve and to the fact that the geothermal industry is ready to scale up globally."
ENGF managing director Oskar Backman added: "We are delighted to be working with Baseload Capital and the other investors on this important energy infrastructure platform.
"We strongly believe in the sector as it offers stable and carbon-free baseload electric capacity to the grid.
"Baseload has demonstrated its capabilities to develop a portfolio of geothermal projects, and we are thrilled to support the company through its next phase in commercializing its pipeline.
"As a business we are committed to help support the green transition and this partnership helps us deliver on our promise.”
________
UK gets nine new offshore wind farms after latest green power auction
Britain is in line for nine new offshore wind farms after the Government’s latest renewables auction, but campaigners fear it may still fall short of clean power targets.
The nine new projects compare to none last year, and include what will be Europe’s largest and second-largest wind farm projects – Hornsea 3 and Hornsea 4 off the Yorkshire coast.
They are part of a new wave of green power projects including onshore wind and solar farms, which officials said will generate enough power for 11 million homes.
Energy Secretary Ed Miliband said the auction had got the offshore industry “back on its feet”, adding that the projects are “essential to give energy security to families across the country”.
Speaking in the Commons, he described the latest auction as the “most successful… in British history” and a “major step forward in our mission to make Britain a clean energy superpower and help Britain get off the rollercoaster of volatile global gas markets”.
He also claimed the previous government’s “nine-year ban destroyed the pipeline of projects for onshore wind”, adding the Labour Government will seek to rebuild this.

https://www.msn.com/en-us/money/mark...pU41B?ocid=Bir
________
New energy facility and other cost saving measures after Trust awarded PS16.2m
A new energy facility, solar panels and insulation measures will be introduced at Royal Shrewsbury Hospital (RSH) as part of a Ł16.2 million investment.
The Shrewsbury and Telford Hospital NHS Trust (SaTH), which runs RSH, secured the funding through the Public Sector Decarbonisation Scheme. It will be used to replace and upgrade the current ageing heating infrastructure with modern and more sustainable energy sources.
The project will see the installation of heat pump technologies which will provide low carbon heating, hot water and chilled water to buildings across the hospital site. This will enable the Trust to remove the old steam boilers and associated gas-fired equipment and fully “de-steam” the hospital estate.
A range of energy conservation measures such as solar panels, which will be installed on the available roof spaces, the upgrade and optimisation of the building energy management systems, upgrades of roof and pipework insultation, and the replacement of air handling fans units with low-energy fan systems, which will reduce the site’s energy consumption, will also be funded by the grant.
These improvements will create a better experience for both patients and staff. When the work is complete, the investment could save the Trust, which also runs Princess Royal Hospital (PRH) in Telford, an estimated Ł1m a year in energy costs and will reduce the hospital’s emissions by over 3,000 tonnes of carbon each year.
Inese Robotham, Assistant Chief Executive and Chair of the Trust’s Climate Group, said: “This is fantastic and exciting news for the Trust, and we’re delighted to have secured this funding. The Trust is committed to continuous investment in both our hospitals, particularly in areas which support greener solutions.
“This aligns with our vision of sustainable health services and more modern facilities that will improve the experience of our patients and colleagues.”
John Runniff, Account Development Director for Vital Energi, said: “Vital Energi are delighted that our proposed solution was selected by the Trust and we are excited to be delivering this innovative carbon reduction project at Royal Shrewsbury Hospital. The complex and robust solution supports the Trust’s long term sustainability and carbon reduction plans, placing them firmly on the path to a net zero future.”
The project received grant funding from the Public Sector Decarbonisation Scheme (PSDS), which is administered by Salix on behalf of the Government’s Department for Energy Security and Net Zero (DESNZ).
Director of Programmes at Salix Ian Rodger said: “The Public Sector Decarbonisation Scheme is having a huge impact across the country, and we are delighted to be working with the teams at Royal Shrewsbury Hospital.
“The funding will not only deliver a more energy efficient hospital and support the Trust’s carbon reduction plans, but it will help create a more comfortable environment for patients, staff and visitors.
“Our teams will work closely with the Trust as continues its journey to a net zero future.”
This investment will support the Trust’s Estates decarbonisation Strategies, Green Plan and national NHS ambitions of reaching net zero by 2040. Decarbonising the public sector is expected to save an estimated Ł650m per year on average to 2037.
Lee Podger, Carbon and Energy Fund (CEF) Client Relationship Manager, said: “The Carbon and Energy Fund (CEF) were extremely pleased to be asked by the Trust to lead on the development of their PSDS Salix application and subsequent procurement of their energy efficiency and energy generation project. Working closely with the Trust and CEF framework contractors, the Trust has chosen a solution that has created an innovative carbon reduction project.”
A grant of Ł300,000 was also awarded by NEEF (National Efficiency Energy Fund) and work at RSH, which included solar panels on the Copthorne Building, SaTH Education Research and Improvement Institute and renal and admin hub, as well as LED lighting, is now complete.
The Trust is also planning projects to install solar panels and LED lighting at PRH once additional funding is secured.
_________
CIP delivers first power from Buffalo Plains
Copenhagen Infrastructure Partners (CIP), on behalf of its Copenhagen Infrastructure IV (CI IV) fund, announced that power from the Buffalo Plains was delivered to the Alberta grid for the first time.
The first turbine on Buffalo Plains was installed in April 2024 and more than a third of the wind turbines are currently installed. Completion of the remaining installation work is expected in the 4Q24 followed by full grid connection. Once fully operational, Buffalo Plains will consist of 83 turbines with a total capacity of 495 MW, providing clean energy to approximately 240 000 households in Alberta, Canada. The project is being delivered in collaboration with Siemens Gamesa and Borea Construction.
“We are very pleased to have reached this important project milestone on Buffalo Plains,” said Tim Evans, Partner and Head of North America at CIP. “The successful delivery of first power demonstrates CIP’s unique ability to execute on large and complex infrastructure projects that will provide local jobs and clean, renewable wind energy for many years to come.”
Buffalo Plains is an important part of the 29 GW+ portfolio of renewable generating assets – including onshore wind, offshore wind, solar PV, battery storage, pumped storage hydro, and transmission – that CIP has in development, construction or operation across North America. In Canada, CIP currently has the country’s largest solar projects and wind projects (by MW) under development.
________
Safe Passage: Innovative Hydro Turbines Do No Harm
Hydropower plants can negatively impact the ecosystem. Here’s how Natel Energy is helping negate some of these impacts.
Hydropower plants produce energy without carbon emissions, but they can negatively impact the local ecosystems. Damming or diverting natural water resources disrupts fish habitats and migration. Further, fish are killed when they swim through turbines and other underwater equipment.
California-based Natel Energy has developed a turbine to greatly reduce fish deaths. The company claims its FishSafe Restoration Hydro Turbines (RHT) allow for 98-100% safe fish passage.

How Does the Technology Work?
Conventional hydro turbines often use screening to prevent fish from entering turbines. However, screens can be ineffective or trap fish so they can’t escape predators.
Instead, Natel Energy focused on redesigning the turbine blades. They created a curved blade with a thicker leading edge. The change pushes water to the front, creating a zone where it stays stagnant and allows fish to pass safely by the moving components.
Additionally, the curved blades prevent fish from taking direct hits even if they get too close. Natel Energy tested its technology with several species, finding that it worked better for protecting fish than similar designs.

However, the technology only applies to fish engaged in downstream migration. Additionally, the turbines are slightly less powerful than some conventional ones, which could make decision-makers less willing to use them.
The propeller is designed for any size hydro turbines in plants up to 40 m (130 ft) in head. Peak hydraulic efficiency measures over 90%. The blades are abrasion-resistant.
People familiar with fish-safe turbine designs say these options are critical at facilities without ramps or bypasses that are sometimes impractical to include due to insufficient space surrounding the hydropower system.
https://eepower.com/news/safe-passag...es-do-no-harm/
_________
More kids are riding electric school buses this fall
More students than ever are headed to class in an electric school bus this fall as school districts race to take advantage of unprecedented government funding to replace their diesel fleets.
Why it matters: Exhaust from diesel buses is linked to serious health and development conditions for children, especially in low-income communities.
- The growing electric bus movement, fueled by a plethora of state and federal incentives, promises to reduce tailpipe emissions and improve kids' health, too.
- Electric school buses can also act as giant batteries to store surplus energy when not in use. That means cash-strapped districts can earn money from their parked buses by selling power back to the grid during times of peak demand.
Where it stands: Almost 235,000 U.S. students currently ride electric school buses, according to the World Resources Institute, whose Electric School Bus Initiative closely tracks adoption rates.
- That's still a tiny fraction of the 21 million kids who take the bus to school in the U.S. each day.
- More than 90% of current buses run on gasoline or diesel fuel. Most others run on propane or compressed natural gas.
State of play: Congress set aside $5 billion over five years to replace diesel-burning school buses under the 2021 Bipartisan Infrastructure Law.
- The Clean School Bus Program, administered by the Environmental Protection Agency, prioritizes school districts in low-income, rural and Tribal communities.
- So far, the EPA has spent $2.8 billion to fund more than 8,000 electric school buses.
- Nearly 1,300 school districts in 49 states, four U.S. territories, Washington D.C., and 55 Tribal communities received funding, and many more are in line for awards in future years.
By the numbers: There are roughly 12,000 committed electric school buses in the U.S., including those funded, ordered or delivered, as well as the ones currently on the road.
- That's 2.5% of the roughly 493,000 school buses in the U.S.
- An electric school bus costs about $370,000, more than triple the price of a traditional diesel bus.
- While the lifetime savings on fuel and maintenance averages $100,000, the remaining price gap would be unsurmountable for many school districts without government subsidies.
Follow the money: The EPA's Clean School Bus Program has funded about two-thirds of the 12,000 committed electric buses.
- Many states offer generous rebates, too, including California, Colorado, New York, Connecticut and others.
- Some local utilities also provide financial incentives to support school bus electrification.
- Another $40,000 rebate for electric commercial vehicles, including school buses, was included in the 2022 Inflation Reduction Act.
- Add it all up and electric school buses are practically free.
Yes, but: The arrival of electric buses has stirred controversy in some communities, where EVs have been politicized.
The intrigue: New technology — whether it's electric cars or the latest smartphones — often starts with wealthy early adopters.
- But in this case, the cleanest, most advanced school buses in America are being deployed primarily in districts with low-income households in non-white neighborhoods that also have the worst pollution, per WRI.
- One example: Salt Lake City used a combination of state and federal funding to buy 12 electric buses, deployed mostly in its Rose Park neighborhood, which is less affluent and suffers disproportionately from poor air quality.
What we're watching: With just two years left in the Clean School Bus Program, the question is whether the next Congress will extend the funding so more diesel school buses can be retired.
https://www.axios.com/2024/09/04/ele...l-bus-adoptionLast edited by S Landreth; 06-09-2024 at 04:39 PM.
-
13-09-2024, 04:49 PM #756
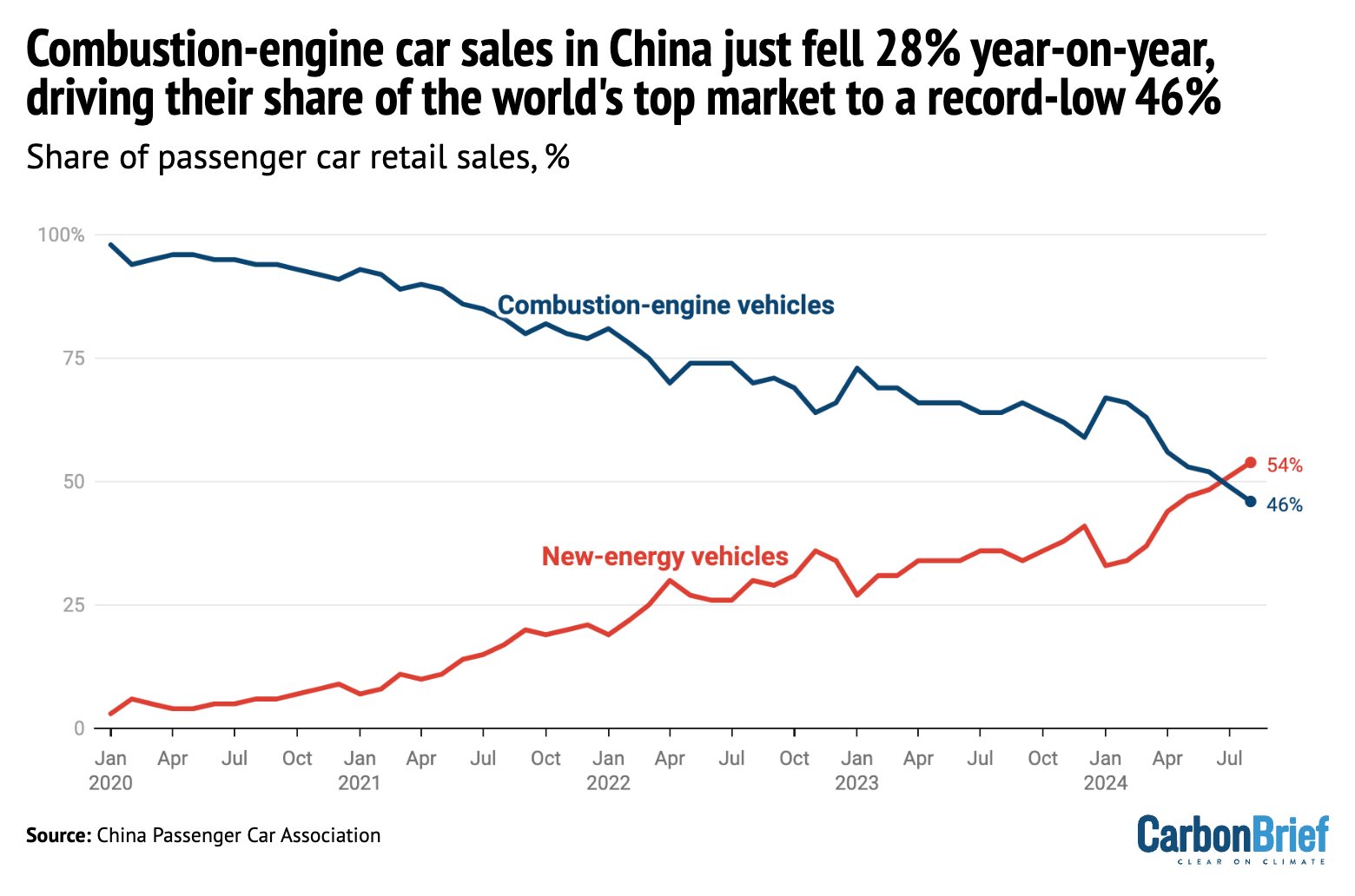
Simon Evans: NEW: Conventional combustion-engine car sales just fell 28% year-on-year in August, driving their share of the world's top auto market to a record-low 46%
NEV sales, including BEV and PHEV, climbed 43% year-on-year in August – and 35% in 2024ytd
The 54% market share for NEVs in August was up 17% percentage points on a year earlier (!)
PHEVs, inc EREVs, are the fastest-growing segment of the NEV market:
PHEVs: 440k sales +97% yoy
BEVs: 530k sales +19% yoy
https://twitter.com/DrSimEvans/statu...10965002396075
_________
AIDA Cruises tests renewable biofuels supplied by VARO EnergyNews
In the port of Rotterdam yesterday, AIDA Cruises refueled its AIDAprima cruise ship for the first time using 100% renewable Bio Marine Fuel as part of a pilot project to evaluate the fuel performance in regular ship operations for potential for future use.
The blended biofuel is produced entirely from advanced feedstocks organic waste or residue. The Bio Marine Fuel (BMF100) sustainable biofuel supplied by VARO Energy is expected to reduce greenhouse gas emissions minimum of 85% compared to conventional fossil fuels.
"We are focused on identifying advanced fuels and technologies we can use to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. In our search for the fuel mix of the future, we have been gathering valuable experience through trials using various biofuels since 2022, and we continue to closely cooperate with experts from industry and science to develop new approaches to continuously reduce emissions," explains AIDA Cruises President Felix Eichhorn. "In order to achieve a sustainable future, we need a growing supply of biofuels and other low-carbon alternative fuels – available globally at scale and at marketable prices," Eichhorn continues.
After refueling in Rotterdam, AIDAprima will test the new biofuel during regular ship operations on upcoming voyages from Hamburg through the fjords of Norway. The fuel performance will help determine its potential for future use across the AIDA fleet.
"Since 2019 VARO has successfully developed, blended, and supplied a diverse range of biofuels for marine bunkering. Our products include B30/B100, HVO (up to 100 percent) and various low FAME biofuel blends. We are excited to supply AIDAprima, working with AIDA and Carnival Corporation & plc, the world's largest cruise company. This operation, taking place near our Rotterdam office, reflects our ongoing efforts to support marine customers in their decarbonization journey as the industry adapts to new regulations. We look forward to continuing our work with AIDA and expanding our biofuel offerings in the ARA region and beyond," commented Sacha Konan, Country President / VP Commercial Benelux & France at VARO Energy.
__________
In the salt deserts bordering Pakistan, India builds its largest renewable energy project
Rising from the bare expanse of the large salt desert that separates India from Pakistan is what will likely be the world's largest renewable energy project when completed three years from now.
The solar and wind energy project will be so big that it will be visible from space, according to developers of what is called the Khavda renewable energy park, named after the village nearest to the project site.
At the site, thousands of laborers install pillars on which solar panels will be mounted. The pillars rise like perfectly aligned concrete cactuses that stretch as far as the eye can see. Other workers are building foundations for enormous wind turbines to be installed; they also are transporting construction material, building substations and laying wires for miles.
When completed, the project will be about as large as Singapore, spreading out over 726 square kilometers (280 square miles). The Indian government estimates it will cost at least $2.26 billion.
Shifting to renewable energy is a key issue at the ongoing COP28 climate summit. Some leaders have voiced support for a target of tripling renewable energy worldwide in any final agreement while curbing use of coal, oil and natural gas, which spew planet-warming gases into the atmosphere.
What makes this heavy industrial activity peculiar is that it's taking place in the middle of the Rann of Kutch in western India’s Gujarat state. The Rann is an unforgiving salt desert and marshland at least 70 kilometers (43.5 miles) from the nearest human habitation but just a short army truck ride away from one of the world’s most tense international borders separating the two South Asian nations.
GROUND ZERO OF INDIA'S CLEAN ENERGY TRANSITION
When The Associated Press visited the renewable energy park, two days of unseasonal heavy rains had left the ground muddy and water logged since the only escape for water in this rough terrain is evaporation. This made it even harder for the workers to do their job.
Notwithstanding the tough conditions, an estimated 4,000 workers and 500 engineers have been living in makeshift camps for the better part of the past year toiling to get this project up and running.
Once completed, it will supply 30 gigawatts of renewable energy annually, enough to power nearly 18 million Indian homes.
As India aims to install 500 gigawatts of clean energy by the end of the decade and to reach net zero emissions by 2070, this project site will likely contribute significantly to the world’s most populous country’s transition to producing energy from non-carbon spewing sources.
___________
Honda to Enter EV Market, Aims for 1/3 Sales by 2030

Honda Motorcycle & Scooter India is looking to enter the electric vehicle segment this fiscal and eyes one-third of its overall sales to accrue from the segment by 2030.
Speaking to reporters on the sidelines of 64th SIAM annual session here, HMSI Director (Sales and Marketing) Yogesh Mathur said the company will be entering the EV segment this fiscal.
He noted that the contribution of electric two-wheelers in overall two-wheeler sales was continuing to grow.
"And what we understand is that by 2030 there will be a major shift towards EVs and we have announced that by 2030 in our lineup also..one-third at least will be coming only from EV models," Mathur said.
The EV model is being developed jointly by HMSI and Honda teams, he added.
On capacity utilisation at its plants, Mathur said the company's plants were currently running at full capacity.
The company will be tweaking the production capacity further in terms of per day basis, he said.
HMSI has an installed production capacity of 62 lakh units per year.
On being asked if the company plans to come out with a new manufacturing facility, Mathur said: "We are studying those options. So all those options are also in pipelines".
On sales expectations in the festive season, he said it could turn out to be one of the best years for the two-wheeler industry.
When asked when the industry can get back to the sales peak of 2018-19, Mathur said: "It should take around three to four years".
___________
EIB and Development Bank of Southern Africa increase support for private sector renewable energy to € 600 million/ ZAR 11.9 billion
EIB and DBSA have committed an additional € 100 million (ZAR 1.98 billion) each to the initiative launched in 2022.
The initiative supports private sector solar and wind energy projects in South Africa, contributing to reliable clean energy and job creation.
Projects supported are expected to produce 384 MW of new renewable energy capacity.
The European Investment Bank (EIB) and the Development Bank of Southern Africa (DBSA) have further boosted their support for renewable energy projects in the private sector, aiming to increase clean energy generation while supporting new jobs.
EIB and Development Bank of Southern Africa increase support for private sector renewable energy to € 600 million/ ZAR 11.9 billion - Agenparl
___________
Israeli renewable energy company Arava Power says its first US solar power project SUNRAY has officially begun commercial operations in Texas.
The project was developed in collaboration with top Israeli oil and gas retailer Paz Group, and funded in partnership with Israeli insurance company Menora Mivtachim, at a total cost of $330 million.
SUNRAY covers an area of some 1,200 acres and is being leased for a cumulative period of 50 years. The site contains more than 500,000 solar panels and is expected to produce 515 gigawatt-hours of electricity per year.
This will prevent the emission of 225,000 metric tons of carbon dioxide and provide clean electricity to 43,000 homes in the San Antonio area every year.
https://nocamels.com/2024/09/israeli...power-project/
___________
Switzerland unveils innovative floating solar project in the Alps
Switzerland is setting a new standard in renewable energy with its innovative floating solar panel project in the Alps.
The country is gaining international attention for this cutting-edge photovoltaic initiative, which utilizes floating solar panels to capture solar power in high-altitude reservoirs. This advancement is particularly notable as nations worldwide increasingly embrace renewable energy sources like wind and solar to reduce fossil fuel dependency, News.Az reports citing foreign media.
Switzerland is taking a significant leap forward by adopting floating solar panels, a relatively novel technology that promises both environmental and practical benefits. Since 2019, Romande Energie, a Swiss company, has been spearheading an ambitious project on Lac des Toules, a high-altitude reservoir located approximately 1,810 meters above sea level.
This reservoir now hosts a floating solar farm with a capacity of nearly 448 kW, featuring 35 platforms of bifacial solar panels. Remarkably, these panels cover just two per cent of the reservoir’s surface area. The floating platforms are designed to stay on the water from June to December, coinciding with the reservoir’s full capacity due to snowmelt, and are positioned on the ground from January to May. Research conducted by the Zurich University of Applied Sciences highlights the project’s impressive environmental impact.
The floating solar panels are expected to recover their energy investment in just over two years. Additionally, the system demonstrates a significant reduction in carbon footprint, emitting approximately 94 grams of carbon dioxide per kWh—substantially lower than traditional solar installations.
Switzerland’s floating solar project on the Alps marks a major advancement in sustainable energy solutions. By utilizing high-altitude reservoirs, the country is not only generating clean energy but also addressing potential water evaporation issues during drought periods. This innovative approach positions Switzerland at the forefront of the global energy transition, offering valuable insights and benefits for future renewable energy projects.
https://news.az/news/switzerland-unv...ct-in-the-alps
-
20-09-2024, 03:41 PM #757
Big Oil, clean energy chart future of geothermal energy
The future of an emerging form of American clean energy could be built on an unexpected foundation: technology and experience from Big Oil.
At least, that’s the hope of representatives of major oil companies, tech startups, scientists and climate groups who met in Houston this week to launch a $10 million series of summits.
Their goal: to use the technology of oil and gas — an industry whose products are the primary force driving the earth’s major natural systems toward collapse — to build a new stalwart of the American power sector.
That emerging force is geothermal energy, which uses heat from deep underground to generate power.
The Energy Department has argued geothermal, which offers a way to produce on-demand, zero-carbon energy without major technological advancement, could power as many as 260 million homes by midcentury.
In April, the agency projected that only $25 billion in public-private investment — less than the cost of a recent nuclear project — spent by decades’ end could begin a rolling snowball of innovation that makes that future a reality.
These advantages — and a wave of federally-funded research that has proven early-stage geothermal technology — have fueled the launch of a bustling Texas startup scene. On Tuesday, Houston-based startup Fervo announced that it had raised $100 million toward a project contracted to put 400 megawatts of geothermal energy on the Nevada grid by later this decade.
And last month, Sage Geosystems, which is also based in the city, signed one deal with Meta to provide underground energy storage to power company data centers and another to put electricity directly into the Texas grid — both efforts to use geothermal-adjacent technology to compete in Texas’s booming battery storage market.
Geothermal resources lie beneath the surface in other areas of the country as well, waiting to be tapped: In June, Project InnerSpace, a leading geothermal advocacy group, released a widely-circulated map showing the vast potential for geothermal energy across the U.S.
The current summits are particularly focused on next-generation geothermal — which uses fracking technology to excavate artificial reservoirs in the hot, dry rock thousands of feet underground.
This is a method that offers significant — if still unproven — advantages in the current energy landscape. Next-generation geothermal can produce electricity when solar and wind are inaccessible, and it lacks the mineral supply chain problems of batteries, the river-reliance and seasonal instability of hydropower and the price swings and pollution of fossil fuels.
It also offers the only current means, aside from nuclear power, of generating on-demand electricity on the specific spot where it’s needed without heating the climate.
Even with its apparent potential, however, the industry also faces roadblocks and bottlenecks that are holding it back from fully taking off. The Geothermal Energy from Oil and Gas Demonstrated Engineering (GEODE) consortium, which launched this week, brings together representatives of the industry, policy and academic worlds to identify those challenges — and determine how to remove them.
The consortium brought together “the best of the energy industry,” said Jamie Beard, founder and director of Project InnerSpace, which is co-running the Department of Energy-funded project.
There were representatives of the first generation of geothermal startups: companies like Sage, Fervo and Bedrock Energy; scientists from national laboratories like Los Alamos and the National Renewable Energy Laboratory; labor leaders from groups like the Texas Climate Jobs Project and the International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers.
And there were also representatives of major oil companies like Oxy, BP, Devon or Chevron — where some executives see geothermal, with its heavy reliance on drilling, as the most obvious renewable for their companies to focus on as they look to expand their energy portfolios beyond fossil fuels.
As things currently stand, the geothermal sector has struggled with the common problems of emerging industries: the difficulty of raising sufficient money for projects that, however promising, have yet to prove themselves.
As GEODE working groups this week concluded, many of the industry’s handicaps relate to this lack of a proven track record, an obstacle that previously confronted wind power in the early 2000s and solar in the 2010s.
With the first commercial geothermal projects still in their infancy, there isn’t enough data to persuade financiers to invest in new projects that would help provide more data. And without a clear demand for geothermal jobs, workforce training programs aren’t turning out the skilled laborers that would allow the sector to expand — which could, in turn, create more jobs.
Other potential problems relate to the sector’s current reliance on water — an issue in Texas and the West, where the nation’s best geothermal resources coincide with diminishing rivers and groundwater.
And geothermal faces cultural and social issues, as well: concerns related to earthquakes and water pollution, popular distrust and dislike of oil and gas companies and fears that a new geothermal drilling revolution will replicate the environmental damage and injustices of the shale boom that began in the mid-2000s.
That boom made the U.S. the world’s leading oil and gas producer. But that outpouring of oil and gas relied on wells and pipelines that often went — and still go — into the ground without the consent of landowners, and at the cost of water pollution, cancer risk and social conflict.
These are the kinds of problems that GEODE is intended to get ahead of. Over a year of meetings across the country, GEODE aims to build a clear sense of the technical, social and financial issues holding the industry back — and the ways that existing knowledge from oil and gas can help address those challenges.
Then — if granted in future appropriations by Congress — the program would make up to $155 million in additional Energy Department-funded grants to companies and research institutions seeking to solve those problems.
Its ultimate goal is to create a series of new first-of-a-kind geothermal technology demonstrations by the end of the decade.
This builds on a productive model of public-private collaboration that has helped get geothermal to a place where big commercial deals are even possible. Fervo’s recent deals, for example, have relied heavily on — and contributed to — research done in southern Utah by the Frontier Observatory for Research in Geothermal Energy (FORGE) program.
Much of the rapid progress the industry has made in recent years has relied on the decades-old tradition of knowledge transfer between oil and gas and geothermal.
The diamond-cutter drill bits currently used to drill for oil and gas, for example, were originally developed by federal researchers in the 1980s for geothermal. In the present day, meanwhile,oil industry’s expertise that could be helpful to geothermal extends from the resolutely technical — methods of horizontal drilling, say — to the more organizational.
Oil and gas companies have learned over the course of decades how to get big, risky projects financed, and how to integrate diverse teams of geologists, engineers and surveyors to drill wells quickly — all of which geothermal developers would have to do to keep costs down and projects attractive to investors.
In an interview with The Hill on Thursday, Fervo CEO Tim Latimer praised the GEODE effort, which his company is participating in.
“There’s a lot of technical resources in the oil and gas industry that can be systematically applied to the geothermal sector,” Latimer told The Hill. “And we’re really excited there’s a consortium there pushing it forward.”
Despite a level of initial “distrust,” Chad Timken of the Society for Petroleum Engineers (SPE), which is co-running GEODE, told The Hill, “as the days have gone on, it’s been, ‘Okay, we’re more similar than not.’”
In a potentially discordant note for the climate movement, Timken raised the possibility that the knowledge transfer could be two-way. “There are some reservoirs that are extremely hot that oil and gas hasn’t messed with because we don’t have the technology to drill that deep,” Timken added.
The summit “is for technology transfer from oil and gas to geothermal,” he said. “But at the same time, it’s like, ‘What can oil and gas take away from geothermal that also helps that industry as well?’”
Dana Otilio, a spokesperson for SPE, said that Timken, despite his coordinating role in GEODE, doesn’t speak for the organization as a whole, and his “in-the-moment, casual and personal” comments were “not based on any SPE position.”
“I can assure you, as an SPE spokesperson, that SPE does not have an ulterior motivation nor any alternative plan for our involvement in GEODE” beyond the transfer of oil and gas knowledge into geothermal energy, Otillio added.
In an interview on Thursday, Latimer of Fervo said he hoped the consortium looked beyond exploration and drilling — areas where recent advances have rapidly cut costs — and also focused on how to produce power from geothermal wells more efficiently and at lower cost.
Fervo wants help in that domain because — as company leadership noted in a presentation last week — those “above ground” costs are now the biggest ones facing the company.
“We need more efficient cooling technologies that don’t involve water, more efficient real-time monitoring, production and injection pumps that are designed for geothermal,” he said.
In addition to technical challenges, the group will have to confront political ones.
“It is a situation where you have two industries who maybe haven’t always gotten along — or two ideologies that don’t seem to really mesh very well,” Timken of SPE said.
Project Innerspace director Beard has argued that geothermal, which is currently the form of geothermal energy with by far the most bipartisan support, risks being torn apart by American political polarization if the sector isn’t proactive in addressing divisions between the renewable and oil and gas worlds.
As such, some of that first $10 million GEODE participants put toward launching the summits went to hire a conflict management group with experience working in conflict zones from postwar Guatemala and Northern Ireland to post-apartheid South Africa.
“We’re coming from different cultures, different levels of trust, different levels of respect,” said Harvard psychologist Josh Greene in an address at the end of the second day.
“I think that if this is going to succeed, it’s going to be because there has been a collaborative culture that embraces the entire group.”
__________
Solar for All
Under the $7 billion Solar for All program, the 60 grant recipients will create new or expand existing low-income solar programs, which will enable over 900,000 households in low-income and disadvantaged communities to benefit from distributed solar energy.
Collectively, these programs will deliver on the Greenhouse Gas Reduction Fund’s objectives by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and other air pollution, delivering cost savings on electric bills for overburdened households, and unlocking new markets for distributed solar in states and territories that have never had statewide low-income solar program before.
The 60 applications selected to receive awards include 49 state-level awards, six awards to Tribes, and five innovative multistate awards, spanning the entire country. View the 60 grant recipients in this table: in the link
__________
India Secures $386 Billion For Renewable Energy Push; Reliance And Adani Pledge Major Commitments
India is set to connect a record 35 gigawatts (GW) of solar and wind energy to its power grid by March 2025, as part of its efforts to accelerate clean energy adoption after missing its 2022 renewable energy target. This move comes as the nation, the world’s fastest-growing major economy, aims to achieve its ambitious 2030 clean energy goals.
Bhupinder Singh Bhalla, the top official at India’s Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, revealed that the country will add 30 GW of new solar capacity and 5 GW of wind capacity during this fiscal year. This marks a significant increase, especially after the slowdown in large solar farm projects in recent years.
In the first five months of the current fiscal year (April to August 2024), India added 10 GW of renewable energy capacity, bringing the total to about 153 GW. Bhalla expressed optimism, stating that next year’s additions would surpass the current year’s.
The country, which is the third-largest solar power producer globally, also sees growing demand for battery-linked storage projects, with more tenders for such initiatives expected soon. Despite its progress, India remains 13% short of its 2015 Paris Agreement pledge to achieve 175 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2022.
As the world’s third-largest greenhouse gas emitter, India faces the challenge of ramping up its clean energy efforts. To meet its 2030 target of 500 GW of non-fossil power capacity, the nation will need to increase its annual renewable capacity additions by 30%.
To support these efforts, Indian financial institutions have pledged $386 billion for renewable energy projects by 2030. Major Indian conglomerates have also made significant commitments, with Reliance Industries promising 100 GW of additional renewable capacity by 2030, and Adani Green Energy committing 38.8 GW.
These pledges underscore India’s growing focus on clean energy as it seeks to balance its energy needs with environmental sustainability, despite its continued reliance on coal to meet surging power demand
____________
Newly developed electrolyte could boost renewable energy storage
Renewable energy sources like wind and solar are critical to sustaining our planet, but they come with a big challenge: They don't always generate power when it's needed. To make the most of them, we need efficient and affordable ways to store the energy they produce, so we have power even when the wind isn't blowing or the sun isn't shining.
Columbia Engineering materials scientists have been focused on developing new kinds of batteries to transform how we store renewable energy. In a new study published in Nature Communications, the team used K-Na/S batteries that combine inexpensive, readily-found elements—potassium (K) and sodium (Na), together with sulfur (S)—to create a low-cost, high-energy solution for long-duration energy storage.
"It's important that we be able to extend the length of time these batteries can operate, and that we can manufacture them easily and cheaply," said the team's leader Yuan Yang, associate professor of materials science and engineering in the Department of Applied Physics and Mathematics at Columbia Engineering. "Making renewable energy more reliable will help stabilize our energy grids, reduce our dependence on fossil fuels, and support a more sustainable energy future for all of us."
New electrolyte helps K-Na/S batteries store and release energy more efficiently
There are two major challenges with K-Na/S batteries: They have a low capacity because the formation of inactive solid K2S2 and K2S blocks the diffusion process and their operation requires very high temperatures (>250°C) that need complex thermal management, thus increasing the cost of the process. Previous studies have struggled with solid precipitates and low capacity and the search has been on for a new technique to improve these types of batteries.
Yang's group developed a new electrolyte, a solvent of acetamide and ε-caprolactam, to help the battery store and release energy. This electrolyte can dissolve K2S2 and K2S, enhancing the energy density and power density of intermediate-temperature K/S batteries. In addition, it enables the battery to operate at a much lower temperature (around 75°C) than previous designs, while still achieving almost the maximum possible energy storage capacity.
"Our approach achieves nearly theoretical discharge capacities and extended cycle life. This is very exciting in the field of intermediate-temperature K/S batteries," said the study's co-first author, Zhenghao Yang, a Ph.D. student with Yang.
While the team is currently focused on small, coin-sized batteries, their goal is to eventually scale up this technology to store large amounts of energy. If they are successful, these new batteries could provide a stable and reliable power supply from renewable sources, even during times of low sun or wind. The team is now working on optimizing the electrolyte composition.
________
Norway sees electric cars outnumber petrol models
Norway, one of the world's largest exporters of oil, now has more electric cars on its roads than petrol-driven vehicles.
Of the 2.8 million private cars registered there, 754,303 are now all-electric, compared with 753,905 that run on petrol, according to new figures from the Norwegian Road Federation.
The Nordic country of 5.5 million people is aiming to become the first nation to end the sale of new petrol and diesel cars - by 2025.
Sales of electric vehicles (EVs) have been boosted by tax breaks and other incentives, funded in large part from the money Norway makes out of oil and gas.
Why is Norway the land of electric cars?
The country has a sovereign wealth fund worth more than $1.7 trillion (Ł1.3tn), built up from the proceeds of its oilfields, to act as a "pension fund" for when it runs out.
This cash cushion has made it possible for the government to offer green incentives to motorists, including exempting electric car buyers from sales tax.
In the early days of the EV revolution, Norway's environmental activists even enlisted the help of the country's biggest pop group, A-ha, to promote the use of the vehicles.
Despite this milestone, there is still work to be done. Diesel models remain most numerous at just under one million, but their sales are falling rapidly, says the Norwegian Road Federation.
At present, nine out of 10 new cars sold in Norway are electric vehicles, industry figures indicate. And it's not hard to see why when you consider how much the authorities do to favour them.
Many places offer free parking for EVs and their drivers do not have to pay city tolls.
And while electric car owners in many countries complain about the lack of charging facilities, there are numerous free chargers in every Norwegian town and city, with 2,000 of them in Oslo alone.
https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/cx25ljxpygeo
-
28-09-2024, 04:26 PM #758
· N.S. firm lands US$25 million to capture carbon by mixing limestone in rivers
A Halifax-based company says it expects to receive US$25.4 million for projects aimed at reduce greenhouse gas emissions by mixing crushed limestone in rivers in Canada and Scandinavia.
The first project by CarbonRun has already started, as lime is being added to the West River in Pictou County at Watervale, N.S., about 45 kilometres east of Truro.
The firm says adding lime boosts the river’s capacity to extract carbon dioxide in the water and from the atmosphere around the river. The carbon dioxide combines with the limestone and is carried out to sea, where it will remain in that captured state for tens of thousands of years.
The company said Monday the investment has been arranged by Frontier, a U.S.-based fund that supports carbon-removal projects, with 13 companies planning to pay for carbon credits associated with the projects.
Eddie Halfyard, chief technology officer at CarbonRun, said in an interview his company will receive the money once independent verifiers confirm that its limestone-mixing method has reduced carbon dioxide emissions from the rivers. He said the firm is expecting payments for the West River project at the end of this year.
The 43-year-old co-founder of CarbonRun said the company isn’t releasing the names of other rivers where it intends to operate, as the company wants to first consult with communities and First Nations in the areas.
However, Halfyard said the announcement of the funding agreements shows there is an appetite for the mixing system, which diverts a portion of the river’s flow into the bottom of silo, where the alkaline material is added.
“Rivers and the people that care about rivers now can have a part in global climate change,” said Halfyard.
CarbonRun says that between 2025 and 2029, its liming projects are expected to prevent about 55,000 tonnes of carbon dioxide — roughly the equivalent to the annual emissions from 13,000 cars — from entering the atmosphere.
The company says the addition of limestone is also helping combat the long-term effects of acid rain — created by nitrogen oxide and sulphur dioxide emissions — and as a result is improving Atlantic salmon habitat.
River and lake liming practices were originally developed as a conservation practice aimed at remediating the effects of acid rain, and Halfyard said he’s been involved in this practice since 2005.
Sensors along the river will measure whether the lime dosing is changing the chemical composition of the water as scientists have predicted.
Halfyard said the goal is to attract additional funding from companies that face legal requirements to reduce their greenhouse gases, and are looking to purchase carbon credits.
“That’s our hope. It does take quite a while to be allowed to sell on that market … We hope to be eligible to sell on these markets in the next couple of years,” he said.
https://globalnews.ca/news/10769882/...s-nova-scotia/
_________
· Climate goal to triple global renewable energy by 2030 within reach, IEA says
A goal to triple global renewable energy capacity by 2030 and cut fossil fuel use is within reach, the International Energy Agency said in a report on Tuesday, but will require a huge push to unlock bottlenecks such as permitting and grid connections.
The report comes as leaders from government and business come together at New York Climate week to try to drive forward action against climate change.
Almost 200 countries at the COP 28 climate summit in Dubai last year agreed to reach net zero emissions from the energy sector by 2050 and pledged to triple renewable energy capacity like wind and solar.
The IEA said the renewable energy goal "is within reach thanks to favourable economics, ample manufacturing potential and strong policies," but said more renewable capacity by itself would not slash fossil fuel use and reduce costs for consumers.
“To unlock the full benefits of the tripling goal, countries need to make a concerted push to build and modernise 25 million kilometres of electricity grids by 2030... The world would also need 1,500 gigawatts (GW) of energy storage capacity by 2030,” the IEA said.
Countries at COP 28 also pledged to double energy efficiency measures to help curb power use, but this target will require governments to make efficiency much more of a policy priority.
reuters.com
__________
· Rich countries could raise $5tn of climate finance a year, study says
Rich countries could raise five times the money that poor countries are demanding in climate finance, through windfall taxes on fossil fuels, ending harmful subsidies and a wealth tax on billionaires, research has shown.
Developing nations are asking for at least $1tn (Ł750bn) a year of public funds to help them cut greenhouse gases and cope with the impacts of extreme weather.
Rich countries are mooting potential sums much lower than this, in conventional climate finance such as low-interest loans from the World Bank and similar institutions. But they are also discussing potential new forms of finance, such as a levy on shipping and on frequent flyers. Brazil, which currently has the presidency of the G20, is pushing for a wealth tax of about 2% on billionaires.
Research by the pressure group Oil Change International, published on Tuesday, shows that rich countries could generate $5tn a year from a combination of wealth and corporate taxes, and a crackdown on fossil fuels.
A wealth tax on billionaires could generate $483bn globally, while a financial transaction tax could raise $327bn. Taxes on sales of big technology, arms and luxury fashion would be another $112bn, and redistributing 20% of public military spending would be worth $454bn if implemented around the world.
Stopping subsidies to fossil fuels would free up $270bn of public money in the rich world, and about $846bn globally. Taxes on fossil fuel extraction would be worth $160bn in the rich world, and $618bn globally.
Laurie van der Burg, the public finance lead at Oil Change International, said: “Last year, countries agreed to phase out fossil fuels. Now it’s time for rich countries to pay up to turn that promise into action. There is no shortage of public money available for rich countries to pay their fair share for climate action, at home and abroad. They can unlock trillions in grants and grant-equivalent climate finance by ending fossil fuel handouts, making polluters pay, and changing unfair financial rules.”
Alejandra López Carbajal, the director of Transforma Climate Diplomacy, said: “There is an attempt by developed countries to frame the new climate finance negotiations in a context of public finance scarcity, while in reality there are enough resources to address the climate crisis.”
Finance will be the key issue under discussion at the next UN climate summit, Cop29 in Azerbaijan in November, where a “new collective quantified goal” is expected to be set, under the terms of the Paris agreement.
Governments are meeting this week at the UN general assembly, where the climate will be a high priority. Brazil’s president, Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva, intends to push for changes to the UN under which it would take on far greater responsibility for global climate action, and for other environmental responsibilities including water resources, which suffer from a lack of global governance.
Carbon targets, from both the rich and poor world, are another focus. The International Energy Agency said on Tuesday that replacing dirty fuels, such as biomass, coal and paraffin, used for cooking in large parts of the developing world, would go a long way to meeting the world’s targets on moving away from fossil fuels.
That should be accompanied by higher efficiency standards for buildings and improvements to air conditioning equipment, much of which is grossly inefficient; and in the developed world switching to electricity for heating and vehicle transport.
Sub-national governments, such as regional authorities and cities, also need to do more, according to an annual survey published this week. The Net Zero Tracker report shows there has been a substantial increase in the number of companies, cities and regions setting net zero targets, but four in 10 such entities, even in large countries, do not have such targets.
The electric vehicle company Tesla, for instance, though it claims to be making “meaningful progress on building a plan to achieve net zero emissions as soon as possible”, has not yet published it.
Baku, the capital of Azerbaijan, where Cop29 will be held, has no emissions reduction target. The city’s government has never responded to the annual global CDP survey, which has been asking city authorities about their carbon targets since 2018. Azerbaijan is also one of about 50 countries to lack a national net zero target, though the government is understood to be working on a new climate plan before Cop29.
Rich countries could raise $5tn of climate finance a year, study says | Climate finance | The Guardian
__________
· New wind turbines in Northern Arizona create enough energy for nearly 40K homes
The Babbitt Ranch Energy Center is officially open with 50 new wind turbines. These turbines will help power tens of thousands of homes in Arizona and expand the state’s renewable energy resources.
A renewable wind turbine facility has been on Babbitt Ranches’ Billy Cordasco’s mind for over two decades since he first learned about wind power through a partnership with Northern Arizona University in 2003.
“We were getting to learn about wind and the possibilities of renewable energy as well. It really opens up our imagination to what was possible.” Cordasco said.
So, it was a no-brainer when there was an opportunity to help extend the reach of SRP’s renewable energy.
“Renewable energy, it actually fits in more with the inclusive perspective at Babbitt Ranch like wildlife, recreation, raising of livestock,” Cordasco said.
The project is a partnership with the Salt River Project, Babbit Ranches, the Arizona State Land Department, and NextEra Energy Resources.
The new center will add 161 megawatts of renewable energy to SRP’s grid, producing enough energy to power nearly 40,000 homes and help power Google’s billion-dollar data center in Mesa.
“So being able to 24/7 opportunities for carbon-free energy actually expands the entire needs of a customer,” explained SRP spokesperson Angie Bond-Simpson.
SRP is aiming for net zero carbon emissions by 2050, and she says this facility is a big piece of that puzzle.
“We need a diverse array of renewable resources,” Bond-Simpson said. “So this wind complements our solar portfolio really nicely and it’ll bring nighttime megawatts ours and carbon-free energy to that portfolio.”
The energy center will also benefit local communities by bringing Coconino County $9.5 million in additional tax revenue over its lifetime.
For Cordasco, it’s about the ranch having a purpose. “I don’t care what project Babbitt Ranch is a part of; it’s going to be about the people...”
New wind turbines in Northern Arizona create enough energy for nearly 40K homes
_________
· Vallarta Supermarkets Partners with GreenStruxure® For Onsite Renewable Energy Microgrid
SANTA CLARITA, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Announced today, Vallarta Supermarkets has entered into a contract with GreenStruxure, a leading energy-as-a-service provider, to design, build, operate, and maintain an onsite renewable energy microgrid. This project will deliver clean energy providing 60% of the energy needed to the Vallarta store in Oxnard (2690 E. Vineyard Ave, Oxnard, CA 93036). The project will help Vallarta Supermarket avoid significant energy costs from the first year of operation and limit the impact of rising utility prices. In addition, the project will lower the Supermarket's carbon emissions by 60%, aligning with its sustainability commitment.
“By partnering with GreenStruxure, Vallarta Supermarkets is taking significant steps towards sustainability and reducing our environmental footprint,” said Joel Silva, CFO of Vallarta Supermarkets. “We look forward to offering this service to additional locations in the future.”
GreenStruxure will design, build, operate, and maintain the innovative microgrid solution utilizing solar panels, battery storage, and advanced energy management systems to deliver a clean, reliable, and affordable energy supply. This comes with significant energy cost avoidance and contributes to a greener environment by reducing carbon emissions. Vallarta Supermarkets will receive the outcomes—zero carbon energy, peak demand management, optimized use of energy from the grid and its onsite system, and complete performance
https://www.businesswire.com/news/ho...ergy-Microgrid
-
20-10-2024, 11:40 AM #759
Ebbw Vale: New wind farm gets green light despite objections
A new onshore wind farm has been approved after recent criticism over delays to green energy planning decisions.
RenewableUK Cymru warned Wales risked "falling behind the rest of the UK" in the race to meet clean power targets.
Plans to build five 180m (590ft) high wind turbines on land at Cefn Manmoel common near Ebbw Vale, Blaenau Gwent, have now been given the go-ahead by the Welsh government.
Developer Cenin Renewables lodged plans with the Welsh government's planning inspectors Pedw in August 2023 for the wind turbines, on-site sub-station, underground cables and associated works.
It said the proposed development could generate enough clean electricity to meet the needs of about 20,000 homes.
__________
New York hit its distributed solar goal a year early. Next stop: 10 GW
New York is marking the early achievement of its Climate Leadership and Community Protection Act statutory goal a year ahead of schedule, announcing that 6 gigawatts (GW) of distributed solar have been installed across the state, enough to power more than one million homes.
New York State Energy Research and Development Authority (NYSERDA) president and CEO Doreen M. Harris broke the news onsite at a distributed solar project in New Scotland, NY today. The project, developed by New Leaf Energy and owned by Generate Capital, participates in the state’s Solar for All pilot program with utility partner National Grid, meaning its generation benefits low-income households. The site’s 5.7 MW solar array will generate 6.7 million kilowatt-hours of solar energy annually, powering about one thousand homes.
“New York State has provided a replicable model for others to deliver clean, low-cost renewable energy to more consumers,” asserted Harris. “Our public-private partnerships are the catalysts which have helped us to achieve our 6-GW goal well ahead of target, trailblazing New York’s path to an equitable energy transition.”
Governor Kathy Hochul says this achievement brings New York one step closer to a reliable, resilient, zero-emission grid. The Climate Leadership and Community Protection Act contains goals to generate 70% of the state’s electricity from renewable sources by 2030 and 100% zero-emission electricity by 2040.
“Distributed solar is at the heart of reducing greenhouse gas emissions, expanding the availability of renewable energy, and delivering substantial benefits for our health, our environment, and our economy,” Hochul added.
__________
China unveils kit to test 35MW wind turbines
Chinese manufacturer Sany has unveiled equipment that will allow it to test up to 35MW wind turbines in the latest signal of the stupendous scaling up of technology in the sector.
Sany said that “China’s first and the world’s largest” 35MW test bench was put into operation on Tuesday at its wind power testing centre.
This test bench can simulate the full lifecycle of wind turbines up to 35MW, said the turbine maker.
Equipped with six 100-ton hydraulic cylinders, Sany said it applies multi-directional, coordinated loads across six degrees of freedom, allowing for extreme, multi-axis stress testing.
The test bench can it said also accurately simulate complex weather conditions and extreme working environments, withstanding typhoon-level winds.
By utilising high-intensity accelerated fatigue tests, the test bench can it said simulate 20 years of wind farm operation in just one year.
It can simultaneously perform functional tests, failure limit verification, and design model validation on the entire turbine and key components such as generators, gearboxes and main shafts, said Sany.
“Little by little everybody will know that we are serious about being a major global turbine OEM player,” Sany’s Europe director Paulo Fernando Soares wrote on LinkedIn.
He highlighted Sany’s “new intelligent manufacturing facilities, new products, new first-class testing capabilities” and its ESG programme.
Speaking to Recharge, he added that Sany does not expect there will be 35MW turbines "in the near future, but this kind of investment is for long term."
_________
Final Turbine Installed at Yunlin Offshore Wind Farm in Taiwan
All 80 turbines have been installed at the 640 Yunlin offshore wind farm in Taiwan, being developed by Yunneng Wind Power Co. Ltd., a subsidiary of Skyborn Renewables.
Major offshore construction work at the Yunlin offshore wind farm started in December 2020 with the installation of the first monopile. The first of the project’s 80 Siemens Gamesa 8 MW wind turbines was installed in April 2021.
The 2024 offshore construction campaign commenced in March with the installation of monopiles following the winter break, and by September, all 80 monopiles and the accompanying transition pieces had been installed.
Fred. Olsen Windcarrier (FOWIC) and Shimizu collaborated to handle the transportation and installation of monopile foundations in 2024.
The wind turbine installation vessel (WTIV) Blue Wind, under a contract with FOWIC, was engaged as the installation vessel for both monopiles, in addition to the DLS-4200 of NMDC Energy, and wind turbines, in addition to Cadeler’s Wind Zaratan.
With all foundations, wind turbines, and 78 out of 81 cables in place, the Yunlin offshore wind project is nearing the finish line.
“Thanks to the dedication of our team and partners, the project is on track to deliver on its promise and fully commission the Yunlin OWF by the end of 2024”, said Skyborn Renewables.
Renewable energy from the wind farm is provided to Taiwan Power Co. under two 20-year power purchase agreements (PPAs).
Located in the Taiwan Strait, the project is already making a significant impact, having fed over 1.6 TWh of renewable energy into the grid, according to Skyborn Renewables.
Once completed, Yunlin is expected to provide power to over 600,000 Taiwanese households.
___________
Vale begins testing of Petrobras renewable content Diesel R5 on mining truck

Brazilian iron ore mining giant Vale and oil & gas major Petrobras have announced the signing of a Strategic Alliance Agreement to supply products with a focus on competitiveness and advancing Vale’s decarbonisation agenda. This agreement, which reflects the natural evolution of the protocol of intentions signed by the companies in September 2023, establishes conditions for testing and potentially marketing three strategic products: co-processed diesel with renewable content, natural gas and bunker with 24% renewable content. The products included in the agreement were defined on the basis of joint studies between the companies.
“We are very happy to announce this broad partnership with Petrobras, which brings benefits to both companies and creates value for Brazil,” says Vale’s CEO, Gustavo Pimenta. “The agreement reinforces Vale’s commitment to promoting the decarbonisation of its operations and offering solutions to reduce its customers’ emissions, thus leveraging Brazil’s competitive edge in renewable fuels.”
“We are developing ever greener fuels and honouring our commitment to decarbonise our activities. The partnership with Vale is yet another realisation of Petrobras’ goal of improving production capacity and the company’s logistics structure to deliver to the market greener products such as Diesel R and reinforce our decarbonisation strategy,” says Petrobras President Magda Chambriard.
Diesel R5 is an S10 diesel with 5% HVO (hydrotreated vegetable oil) in its composition. It is produced by co-processing oil derivatives with raw materials of plant origin, resulting in a product with identical technical specifications to mineral diesel and 60% less carbon intensity in the renewable portion.
The agreement provides for collaboration on more competitive models for the supply of natural gas, an essential input for the production of pellets and also iron ore briquettes – a product developed by Vale that contributes to promoting the decarbonisation of the steel industry.
And finally, the alliance provides for Petrobras to sell a very low-sulphur bunker blend with 24% biodiesel for testing on an iron ore transport vessel working for Vale.
The first action under the agreement has already begun with the supply of diesel with renewable content (Diesel R5) by Petrobras. The product began to be supplied to Vale in the second week of October to carry out industrial-scale tests on the Vitória-Minas Railroad and at the Fábrica Nova mine, in the Mariana Complex (Minas Gerais, Brazil), on a Caterpillar 789C mining truck.
-
23-10-2024, 05:49 AM #760
More than 1,000 homes linked to Ł20bn green energy grid expected to be built in Highlands
More than 1,000 new homes are expected to be built across northern Scotland linked to a Ł20bn investment in grid infrastructure needed to meet the UK’s green energy targets.
SSEN Transmission, a subsidiary of the electricity firm SSE, has signed a deal with local councils and housing associations in the Highlands to fund at least 1,000 new properties as well as the refurbishment of existing, unoccupied ones.
The proposal, described by the industry body RenewableUK as “unique and novel”, follows mounting anger in rural areas about the modest financial benefits many communities that host windfarms, overhead lines and electricity substations receive from those projects.
The company, which has a monopoly on building and maintaining the electricity grid in northern Scotland, plans to spend Ł20bn by 2030 to channel power from new offshore and onshore windfarms to be built as part of the UK government’s efforts to decarbonise the electricity supply.
It expects to employ thousands of workers across the Highlands, the Outer Hebrides and Orkney and Shetland – areas suffering from depopulation driven by an affordable housing crisis. That will peak at a workforce of nearly 5,000 people in 2027 and a significant number of those will need new homes.
SSEN Transmission said it will fund the building of those homes by guaranteeing long-lease tenancies as a “pathfinder investment mechanism”, the bulk of them designed as affordable homes for local people.
Alongside other “accommodation villages” using temporary housing, it also expects to refurbish vacant homes and to renovate derelict properties, handing those over to local councils and social landlords after its workforce has left.
Rob McDonald, SSEN Transmission’s managing director, said: “This is a significant and innovative contribution to addressing the housing challenges in the north of Scotland, and it also demonstrates how we can work in partnership to develop imaginative proposals that will deliver new homes and act as a template for other developers.”
The policy, which has been welcomed by Scotland’s housing minister, Paul McLennan, and local council leaders, follows signals from the UK government and is expected to bring in new rules on how the energy industry shares the profits from renewables with local people.
The proposals highlight significant disputes about the definition of community benefit.
James Robottom, the head of policy at RenewableUK, said ministers should be cautious about imposing fixed rules on community benefit because that raised questions for other big infrastructure projects, and could stifle creative ideas.
He said SSEN Transmission’s proposals were the most ambitious and innovative community benefit plan he had encountered. “What this demonstrates is the need for flexibility, in working with the community and understanding what the wider community needs,” he said.
Torcuil Crichton, the Labour MP for Na h-Eileanan an Iar, the Western Isles, and a member of the House of Commons energy committee, said that while these homes were welcome, it was important to distinguish between the benefits from building new infrastructure and sharing in the long-term profits it then generated.
“We should all have a share in the wealth of the wind, which is going to be produced around our coastline,” Crichton said. “The wind belongs to no man.”
-
25-10-2024, 11:45 AM #761
Analysis: Solar surge will send coal power tumbling by 2030, IEA data reveals
Global electricity generation from solar will quadruple by 2030 and help to push coal power into reverse, according to Carbon Brief analysis of data from the International Energy Agency (IEA).
The IEA’s latest World Energy Outlook 2024 shows solar overtaking nuclear, wind, hydro, gas and, finally, coal, to become the world’s single-largest source of electricity by 2033.
This solar surge will help kickstart the “age of electricity”, the agency says, where rapidly expanding clean electricity and “inherently” greater efficiency will push fossil fuels into decline.
As a result, the world’s energy-related carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions will reach a peak “imminently”, the IEA says, with its data indicating a turning point in 2025.
Other highlights from Carbon Brief’s in-depth examination of the IEA’s latest outlook include:
- Renewables will grow 2.7-fold by 2030, short of the “tripling” goal set at COP28.
- Still, clean energy is growing at an “unprecedented rate”, and will overtake coal, gas and then oil, to become the world’s largest source of energy “in the mid-2030s”.
- Low-carbon energy, including renewables and nuclear, will grow 44% by 2030, adding 48 exajoules (EJ) to global energy supplies.
- Global energy demand will only rise by 34EJ (5%) over the same period.
- This means clean energy will push each of the fossil fuels past their peak by 2030.
- Electric vehicles (EVs) are now expected to displace 6m barrels of oil per day (mb/d) by 2030, up from a figure of 4mb/d by 2030 in last year’s outlook.
Despite these changes, the world is on track to cut CO2 emissions to just 4% below 2023 levels by 2030, the agency warns, resulting in warming of 2.4C above pre-industrial temperatures.
It says there is an “increasingly narrow, but still achievable” path to staying below 1.5C, which would need more clean electricity, faster electrification and a 33% cut in emissions by 2030.

The IEA says that China was responsible for 60% of worldwide renewable installations last year – and will add 60% of new capacity out to 2030. This means that by the early 2030s, solar generation in China alone is set to exceed the US’ current total electricity demand.
Fossil fuels peak by 2030
The “age of electricity” will have important implications for the current fossil-fuelled energy system, the report says. These include a reduction in the rate of global energy demand growth, even as demand for “energy services” – such as heat and mobility – rises rapidly in the developing world.
Explaining this apparent paradox, the IEA says that much of the energy released by burning fossil fuels is lost as waste heat. In contrast, a “more electrified, renewables-rich system is inherently more efficient”. This means less energy will be required to deliver the same energy services.
-
29-10-2024, 03:17 PM #762
Singapore Clears $24 Billion Link to Australian Solar
$24 billion renewable energy corridor connecting Australia and Singapore inched closer to completion after developer SunCable received conditional clearance from the city-state.
Singapore’s Energy Market Authority deemed the project technically and commercially viable, SunCable said Tuesday. The company’s Australia-Asia Power Link plans to send 1.75 gigawatts of renewable electricity to Singapore, or about 9% of its current needs, through a 4,300-kilometer (2,670-mile) submarine cable.
The Australia-based project, controlled by tech billionaire Mike-Cannon Brookes, is one of the most ambitious developments globally to supply energy-hungry customers in Asia that don’t have the available land to generate enough renewable power. It won approval for its first stage in August.
“Conditional approval is a vote of confidence from the Singapore government,” Mitesh Patel, SunCable International’s interim chief executive officer, said in the statement. The company now plans to focus on project planning, talks with industrial customers in Singapore and subsea surveys in Indonesia.
Singapore is also holding talks with Australia and clean energy groups on plans to allow the use of credits tied to cross-border electricity imports, the Ministry of Trade and Industry said Tuesday in a statement.
The nation aims to import 6 gigawatts of low-carbon power by 2035, and is working to study pathways to deliver high-integrity certificates linked to clean power generated outside of Singapore.
Development of a credible framework for the credits would help lift demand for cross-border electricity trading and support investment in renewable projects across the region, the ministry said, without giving a timeline for execution of the proposals.
Use of the certificates has been contentious and opponents have argued they’ve often overstated potential climate benefits.
-
09-11-2024, 10:49 AM #763
EU Innovation Fund Awards €51 M to French Tidal Developers
French developers HydroQuest and Normandie Hydroliennes have been announced as the winners in the latest EU Innovation Fund call. 337 applications were received under the Innovation Fund’s 2023 call. In the ‘pilots’ topic, 17 projects have been preselected for a grant, with ocean energy securing 2 projects in France.
HydroQuest, in partnership with Qair, has been awarded for their 17 MW FloWatt tidal farm project. They will install six tidal turbines in Raz-Blanchard in Normandie, France. The FloWatt project—which also received unprecedented financial support from the French Government—should come online in 2026 and will generate enough energy to power 20.000 local homes.
Normandie Hydroliennes has been awarded to install their 12 MW NH1 tidal farm project, also in Normandie’s Raz Blanchard. Composed of four 3 MW turbines—the most powerful tidal turbines to date—it is scheduled for 2028 and will produce 33.9 GWh yearly.
This announcement adds 29 MW to the existing pipeline of publicly supported European ocean energy projects in the next five years, bringing the outlook to 179 MW across 15 projects. This shows once again that funding support is key to unlock farm scale projects and accelerate the industrialization of ocean energy. Innovative renewable technologies, such as ocean energy, will strengthen Europe’s energy security and competitive edge on the global stage.
Ocean Energy Europe CEO Rémi Gruet, said: “These 2 awards are another proof that tidal has reached technological maturity and is on its way to commercialization. These 2 farms will be the largest in the world by the time they hit the water. This is further evidence that the French Government demonstrated great foresight by supporting tidal energy—and that tidal can become the next French industrial success story.”
Attention Required! | Cloudflare
______
Brazil adds 1.2 GW of renewable capacity in Oct 2024
Brazil installed 1,208 MW of solar, wind and hydropower capacity in October, according to data from the nation's power sector regulator Aneel.
Wind farms represent the largest portion, with 19 newly installed facilities accounting for 688.90 MW of the capacity connected to the grid last month. At the same time, 15 solar parks contributed 514.01 MW, while one 5.10 MW small hydropower plant (HPP) was connected to the grid.
In all, the country added 1,533.89 MW in October. The remaining 325.88 MW of new capacity comes from thermal power plants.
During the first ten months of the year, Brazil's electricity system grew by 9,353.76 MW, of which 90.22% came from renewable sources. This capacity increase shows that the electricity mix expansion for 2024 will break records, as was the case in 2023.
On November 1, Brazil had 207,029.1 MW of total installed power generation capacity. The agency noted that 84.80% of the total is produced from renewable energy.
Just a moment...
-
10-11-2024, 08:59 AM #764
Deep Wind Offshore applies for Chile lease
Deep Wind Offshore has applied for an area lease to construct one floating and one bottom-fixed wind farm offshore the Chilean coastline.
Chile’s government aims to have 60% of the country’s electricity generated from renewable sources by 2030, with annual electricity offtake set to be about 65% higher than in 2021.
Deep Wind Offshore said its planned offshore wind projects would be managed and operated locally, with a focus on creating local jobs, working with local suppliers and engaging with the fishing industry.
Deep Wind Offshore applies for Chile lease | Offshore
__________
Entrion Wind bags US patent for FRP base
Entrion Wind has sealed a US patent for its Fully Restrained Platform (FRP) monopile.
Officially granted by the US Patent and Trademark Office on 29 October, the patent is the first of six filed by the company to be awarded.
Entrion Wind’s design of the FRP foundation extends the range of traditional monopile technology to water depths of up to 100 metres, while offering improved economics compared to other foundation systems.
The base integrates proven technologies with the company’s proprietary Top Mooring Assembly (TMA) system. The TMA improves the stability of the monopile by increasing stiffness without impacting installation or operational efficiency.
“This patent is a major achievement for Entrion Wind,” said the outfit’s vice president and co-founder Li Lee.
“Our FRP monopile is designed to deliver exceptional performance in water depths that were previously inaccessible to monopile technology.
“This innovation will help drive down costs and enable the growth of offshore wind energy in deeper waters.”
Entrion Wind continues to test the viability of the FRP monopile with comprehensive feasibility studies and demonstration projects.
Companies can assess whether the FRP monopile concept works for a specific site, estimate impacts on LCOE from CapEx and OpEx, and evaluate project risks and opportunities. Demonstration partners have the opportunity to test the FRP Monopile technology first-hand in the field, as either a full deployment or retrofitted design.
The commercial rollout of the FRP monopile is planned for 2027.
Just a moment...
-
16-11-2024, 11:25 AM #765
CIP launches Voyager Renewables in Oz
Copenhagen Infrastructure Partners, has launched a new platform company in Australia called Voyager Renewables through its Copenhagen Infrastructure V fund.
The new entity is a dedicated onshore renewable energy development player established to originate, develop and build new large-scale wind, solar and battery storage solutions across Australia.
CIP said Voyager Renewables is built with a clear focus on building and maintaining local partnerships that create value from the ground up. Its portfolio of projects aims to deliver 6GW of new capacity across the country over the next 10 years.
Among the sites in the pipeline are the 450MW Sunnyside, the 2GW+ Energy Oasis and the 1GW Western Tablelands wind farms.
Sunnyside is proposed in New South Wales’ South-West Renewable Energy Zone, while the Energy Oasis is an onshore wind project with co-located solar and a battery planned for western New South Wales.
The project would include high voltage transmission to connect large-scale energy solutions to the grid to decarbonise energy intensive industries by the mid-2030s.
Western Tablelands wind farm is in Victoria’s south-west, and would feature a co-located battery storage system.
CIP Australia partner and head Jorn Hammer added: “Voyager Renewables is part of CIP’s global strategy to invest in development platforms. As CIP’s onshore renewables company, Voyager Renewables will develop projects and build lasting partnerships with communities in Australia’s regions.”
Just a moment...
-
19-11-2024, 10:51 AM #766
Wind Used to Be the Darling of Renewables, But There’s a New Source on the Block: Solar Has Overtaken Wind in Record Time in the U.S.
For the first time in U.S. energy history, solar photovoltaic (PV) systems generated more electricity than wind in a single month—and for two months in a row.
It happened this summer. In July and August 2024, solar accounted for 7.41% and 7.42% of electricity generation, respectively. It surpassed wind, which contributed 6.36% and 6.65% over the same period.
While wind still leads in the annual balance (producing 76% more electricity than solar in 2023), the shift appears inevitable.
Uneven growth. This milestone, officially reported by the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), reflects a global trend. Solar power is expanding rapidly, while wind power deployment has slowed.
Even though wind turbines generate more electricity per installation than solar panels, global installed solar capacity has grown by 34% in 2024, compared to just 5% growth for wind.
Why is this happening? The surge in solar power is driven by China’s mass production of solar panels, which has significantly lowered costs. While newer PV modules are less efficient than earlier models, they’re more affordable, and the rise of battery storage solutions has made it easier to capitalize on this increased capacity.
In contrast, wind power faces challenges associated with the size and complexity of wind turbines. These include higher transportation and installation costs, public opposition due to their visual impact, and regulatory hurdles that limit site availability.
Wind Used to Be the Darling of Renewables, But There’s a New Source on the Block: Solar Has Overtaken Wind in Record Time in the U.S.
-
26-11-2024, 04:29 PM #767
Japan may aim to make renewable energy largest power source by fiscal 2040
NHK has learned that Japan's economy and industry ministry is considering devising a scenario in which renewable energy will be the largest electricity source for the country by fiscal 2040.
A council of the ministry is engaged in discussions for a review of Japan's basic energy plan. The review has been prepared every three years.
The current plan says renewable energy, including solar and wind, will account for 36 to 38 percent of the country's energy mix by fiscal 2030.
For a fiscal 2040 scenario, the ministry is considering further raising the share of renewables and making them the largest source of electricity over fossil fuels.
This is in line with the government's goal of achieving net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050.
In a rare move, officials say they may present multiple scenarios. They say it is difficult to predict the future cost of each power source, as well as to foresee the progress of technological innovation at this stage.
The ministry plans to compile a draft of the review next month after holding final discussions on the matter, including the role of nuclear power.
-
30-11-2024, 08:10 AM #768
As Ontario eyes Crown land for renewable energy, parking lots seen as having untapped potential

Ontario recently announced it would be looking to the north for new energy projects, specifically mentioning incentives to "unlock" Crown lands for renewable energy involving wind, solar and biomass.
This comes as the Independent Electricity System Operator (IESO) says demand is increasing faster than previously anticipated and is set to grow by 75 per cent leading up to 2050.
Ontario's plan to meet that demand relies heavily on electricity from nuclear and hydroelectric sources, but solar and wind are expected to play a role as well.
Currently, about one per cent of Ontario's electricity supply comes from solar power, according to the IESO.
That could change in years to come as industrial, commercial and residential consumers participate in the grid via technologies like solar photovoltaic panels.
The case for solar panels in parking lots
Atul Sharma, a renewable energy consultant for Algoma Energy Solutions in Sault Ste. Marie, said parking lots would be preferable to Crown land for solar energy projects.
"There's a lot of space and no shade around," he said.
"We can also tilt the panels southwards with no obstacles."
He added the angling of the panel to maximize sunlight tends to be a challenge when installing them on fixed residential roofs.
According to Sharma, panels on carports in parking lots also help provide shade for cars during heat waves and are sufficiently tilted to avoid snow accumulation.
He said one of the reasons this isn't widespread practice is the initial cost of building a carport over a parking lot to install the panels.
"It's a big initial investment," he said.
City of Greater Sudbury declared a climate emergency 5 years ago. It's not on track to meet its goals
"First we have to build the structure, and that comes with a lot of labour costs. Then we have to cover the whole parking lot.
"But it is worth it because it would produce enough power to supply the shopping malls and the Walmarts," he said.
Sharma said there's a loss of electricity when power is transferred from one place to another, and it would be more efficient to have solar panels closer to buildings, as opposed to out on Crown land.
José Etcheverry is an associate professor at York University and the director of the International Renewable Energy Academy. He was part of the team building one of Canada's first solar photovoltaic parking lots using local materials and labour.
"Two of the things that are needed for these projects are made right here in Ontario," he said, pointing to province's steel industry, solar panel companies, and nascent battery manufacturing capacities.
He says these local solar models would provide the power needed to electrify buses, cars, bicycles, scooters and wheelchairs.
"These could all charge locally in the parking lots that would be full of solar photovoltaics," he said.
Etcheverry says solar is a cheap source of energy, and argues Ontario's turn to nuclear energy and natural gas is a political decision, not a scientific one.
-
30-11-2024, 04:10 PM #769
ABP completes work on PS35m Lowestoft Eastern Energy Facility
Associated British Ports has announced the completion of its new Ł35m offshore energy hub at the UK’s most easterly port.
The Lowestoft Eastern Energy Facility (LEEF) in Suffolk has been purpose-built to support both operations and maintenance activities and the construction of new offshore wind turbines in the North Sea.
ABP has called the fruition of the project, which has received support from the Town’s Fund, "a major milestone in Lowestoft’s energy transition journey".
It said the new site had now been officially handed over by contractors McLaughlin and Harvey, and marked "a new era for Lowestoft and its role in the southern North Sea energy sector".
In October, Lowestoft welcomed the first vessel to the LEEF, which features 345m (1,131ft) of quayside equipped with three 7.5m (24ft) draft deep-water berths with direct supplies of fuel, water and power.
It also has the capacity to accommodate Service Operation Vessels for uninterrupted operations at all tides, together with up to eight acres of storage space and six crew transfer vessels berths.
Julian Walker, chief commercial officer and regional director, Wales and Short Sea Ports, said: "LEEF is a pivotal development for Lowestoft and will help us to meet the growing demands of the offshore energy industry.
"Its completion marks a major milestone in the port’s evolution as a hub for supporting this vital industry and in ABP’s goal of enabling the energy transition.
"LEEF will build on the vital role the Port of Lowestoft is already playing in offshore wind, as the base port for SSE’s Greater Gabbard and SPR’s EA ONE wind farms.
"Its adaptable infrastructure will also ensure ABP’s readiness to support future projects such as Sizewell C and we look forward to continuing to develop for the future in the region through supporting both existing and new projects with world-class facilities."
Adrian Pollock, operations director, civil engineering, from McLaughlin & Harvey, said: "We are proud to have delivered this comprehensive port infrastructure upgrade project.
"Our civil engineering expertise in marine works and collaboration with ABP allowed us to design and deliver a new facility that will help ABP achieve their ambition of offering three berths and heavy lift capabilities for the growing offshore wind and energy sectors at Lowestoft."
-
06-12-2024, 05:00 PM #770
Former Tesco boss wants to send power from Morocco to Great Britain using subsea cable
Dave Lewis says the near-constant stream of clean electricity could supply the grid as early as 2030
In the south-west of Morocco, a sprawl of wind and solar farms stretching across an area the size of Greater London could soon generate the green electricity powering more than 9m British homes.
This is the unflinching vision of Sir Dave Lewis, the former Tesco boss who is hoping to build the world’s longest subsea power cable in order to harness north Africa’s renewable energy sources and power Britain’s clean energy agenda.
If built, a 4,000km cable buried in trenches along the seabed would carry up to 8% of Great Britain’s electricity from renewable energy and battery projects in Morocco’s Tantan province to the Devon coast in under a second.
Combined with Morocco’s perennial sunshine and consistently healthy wind speeds, the project could in theory provide Britain with a predictable and reliable source of renewable energy for about 19 hours a day all year round.
It is an audacious endeavour on which Lewis is willing to stake his reputation. “When people first get to know what we’re doing they say we’re crazy. Then we explain, and they go along this curve until they get to the point where they’re asking ‘Hey, why don’t we do this? Why don’t we already do this?’” he says.
Lewis took up the job of executive chairman at Xlinks, the company behind the plans, in 2020 after carrying out a five-year rescue plan to bring Britain’s biggest retailer back from the brink of collapse. As he prepared to leave the supermarket chain in a “position of strength” he began to look for opportunities to play a role in tackling the climate crisis.
“It would have been very easy to stay at Tesco because in many ways the hard work had already been done. But I do worry about climate change, and I do think we have to do something about it,” he says.
Since then he has been in talks with six energy secretaries over the last four years in the hopes of clinching a deal that would allow the UK-Morocco project to start up by the end of the decade.
The near-constrant stream of clean electricity could begin supplying the energy grid by 2030, he says, in time to power the government’s goal of creating a clean energy system by the end of the decade and meet its new ambition to cut the UK’s carbon emissions by 81% compared with 1990 levels by 2035.
Sir Dave Lewis says the idea that the UK – as an island – should be self-sufficient in just about anything ‘is a fallacy’. Photograph: Martin Godwin/The Guardian
Lewis’s easy confidence in the project, and what it could mean both for the UK and for the Moroccan economy, has not translated into a speedy process of engagement with government officials. It has been more than a year since the government designated Xlinks a project of national significance but Lewis is still waiting for a green light.
Although the project does not need government investment, it does require a contract that guarantees a stable price for the electricity it delivers, which would be paid for through energy bills. Lewis puts this contract price at between Ł70 to Ł80 per megawatt hour (MWh) which is less than the deal struck with the developers of the Hinkley Point C nuclear power plant, and in line with the expected cost of future offshore wind farms.
In the meantime, he has galvanised a team of big-name investors from across the energy industry to help raise the Ł100m required to develop the project. They include the French energy giant TotalEnergies, the Abu Dhabi National Energy Company (TAQA), the investment arm of General Electric, Britain’s Octopus Energy and its founder, Greg Jackson.
Jackson says his only misgiving about the project is that he had not thought of it himself. “If oil and gas companies can build pipelines across the world to pump toxic, leaky substances then we really should be able to run power lines – and it should be easier. It’s eminently feasible but there hasn’t been a political and economic case for it. That’s changing. We have the adoption of renewables across the world. When I heard about Xlinks I wanted to get to know them – I was very keen to personally back them, and Octopus is backing them too.”
Lewis’s lack of energy industry experience is a plus, according to Jackson, who built Octopus Energy from a start-up to a Ł9bn energy company in under a decade following a career in tech. “When you’re an outsider you can see things more clearly. Dave doesn’t look at things through the lens of outdated regulation. This means he can identify the economics that actually work, then hire a team that includes experts who work deep in the plumbing of the industry who can deliver it,” he says.
The delivery of the project is a likely sticking point for the risk-averse government officials. Britain’s chequered history in rolling out major, one-of-a-kind infrastructure projects haunts Whitehall, and Xlinks itself has already been delayed by a year. But Lewis is determined to make the case that delivering the mega-project is simpler than it might appear.
Each element of the project – the solar farms, windfarms, batteries, high-voltage subsea cables – is tried and tested so scaling up its ambition would be a matter of repetition, he says. He has also secured the project’s supply chains in advance, and could source up to 50% of the cable from a planned cable factory in Scotland if it can get the support of the government.
But even among those who believe that the project could be delivered there would likely still be disquiet over relying so heavily on a foreign country for a significant share of Britain’s energy. On this point, Lewis is pragmatic.
“Forgive my simplistic articulation of this, but we’re an island,” he shrugs. “The idea that the UK could be self-sufficient for just about anything is a fallacy. The UK needs to develop these bipartisan relationships, and it needs to invest in, and protect them. But if the benefit is great enough, why wouldn’t you?”
“There may be challenges but you have to ask whether the magnetic north of the idea is strong enough that it’s worth investing your time and your energy in the pursuit of it. I thought it was, and my commitment to that has only grown as I’ve learned more,” he says.
-
10-12-2024, 09:20 AM #771
Japan unveils world's first solar super-panel: More powerful than 20 nuclear reactors
Japan’s audacious strategy for renewables: The PSC technology for polluting China’s new era
Japan is currently utilizing its competitive advantages to lead the rest of the world into the new renewable energy age. Under its revised energy plan, the Ministry of Industry now prioritizes PSCs on Section 0 of its plan wherein Japan aims to develop PSC sections generating 20 gigawatts of electricity equivalent to 20 nuclear reactors by fiscal 2040.
The strategy was designed to be closely aligned with the country’s commitment to net-zero emissions by 2050. At the center of this strategy is Japan’s position as the second-largest iodine producer in the world, a necessary ingredient in the manufacturing of perovskite solar cells.
This would allow an independent supply chain within Japan’s territory, enabling the country to improve its economic security, reduce dependence on foreign origins, and provide forward-looking developments for its domestic industries.
Japan was once the world’s leader in solar panel manufacturing, but its share has fallen to below 1% because of the subsidized competition from Chinese manufacturers. However, Japan can claim that it is again in a stronger position by PSC technology. Supported by the government, Sekisui Chemical Co. is now developing advanced PSC modules for their future application to a broad market in the 2030s.
Changing the game of solar power: PSCs in source redefining urban power generation
All this makes PSCs very different in the sense that they can totally redefine how and where solar energy can be collected. This makes traditional silicon-based panels quite impractical in countries that are densely populated, like Japan, when only large spaces can accommodate them.
With high adaptability and lightness, bendability, and flexibility in manufacturing, PSCs can be integrated with urban environments easily. They can be installed on walls of buildings and windows, on car roofs, and on streetlights, allowing these surfaces to be utilized for energy harvesting.
This invention solves the problem of space limitation in Japan to generate maximum energy in urban areas. The flexibility of PSCs will also allow hybrid systems – wind and solar energy systems – to be installed, further improving renewable energy efficiency. However, obstacles are still in place. Durability limit and high upfront cost are two of the significant concerns for PSCs today, but the technology is improving steadily, with predictions that costs will fall to JPY 10/W by 2040.
Japan’s solar revolution: From 1.9% to 10% energy output in every decade
Ever since the nuclear disaster in Japan in March 2011, the solar energy scene in that country has evolved rapidly. Today, the solar electricity output accounts for almost 10% of the total energy production in the country, compared with the previous year’s share of only 1.9% in 2014.
The current energy plan further aims to push this share by setting the target at 36%-38% of renewable energy sources consumption by 2030 and expects PSC technology to play big in crossing those figures by 2040. The predictions made by the government estimates regarding the cost with time states that PSCs are less expensive with JPY 20/W as of 2025 around which time it will also be lowered significantly after that.
These marks are critically relevant for making PSCs available to a broader audience and using them for more diversified applications. CE certified modules designed for durability and safety are geared to meet the demands of both domestic and commercial users.
With PSC technology, Japan makes serious commitment towards sustainable development. By harnessing its renewable natural resources and encouraging innovation, it positions itself as one of the leading nations in the globe for renewable energy. PSC technology will momentarily be affordable; hence, it will provide energy solutions to Japan while serving as a guide for other countries to prove the premise that wind and solar can create a greener world.
-
10-04-2025, 06:26 AM #772
Analysis: Nearly 60 countries have 'dramatically' cut plans to build coal plants since 2015 - Carbon Brief
Nearly 60 countries have drastically scaled back their plans for building coal-fired power plants since the Paris Agreement in 2015, according to figures released by Global Energy Monitor (GEM).
Among those making cuts of 98% or more to their coal-power pipeline are some of the world’s biggest coal users, including Turkey, Vietnam and Japan.
The data also shows that 35 nations eliminated coal from their plans entirely over the past decade, including South Korea and Germany.
Global coal-fired electricity generation has increased since 2015 as more power plants have come online.
But the data on plants in “pre-construction” phases in 2024 shows what GEM calls a “dramatic drop” in proposals for future coal plants.
The number of countries still planning new coal plants has roughly halved to just 33, with the proposed capacity – the maximum electricity output of those proposed plants – dropping by around two-thirds.
China and India, the world’s largest coal consumers, have also both reduced their planned coal capacity by more than 60% over the same timeframe, from a total of 801 gigawatts (GW) to 298GW.
However, both countries still have a large number of coal projects in the pipeline and, together, made up 92% of newly proposed coal capacity globally in 2024.
_________
Power-sector CO2 hits ‘all-time high’ in 2024 despite record growth for clean energy - Carbon Brief
Global power-sector emissions hit an “all-time high” in 2024, despite solar and wind power continuing to grow at record speed, according to analysis from thinktank Ember.
Emissions from the sector increased by 1.6% year-on-year, to reach a record high of 14.6bn tonnes of carbon dioxide (tCO2).
This increase was predominantly due to a 4% growth in electricity demand worldwide, leading coal generation to increase by 1.4% and gas by 1.6%.
Embers’ analysis finds that the increase in fossil-fuel generation was, in particular, due to hotter temperatures in 2024, which drove up electricity demand in key regions such as India.
Clean electricity generation grew by a record 927 terawatt hour (TWh), which would have been sufficient to cover 96% of electricity demand growth not caused by higher temperatures.
Despite the increase in emissions in the short-term, this “should not be mistaken for failure of the energy transition”, notes Ember, but a sign the world is nearing a “tipping point” wherein changes in weather and demand hold a particularly strong sway.
Clean-power growth
Low-carbon energy sources – renewables and nuclear – provided 40.9% of the world’s electricity in 2024, according to Ember.
This is the first time they have passed the 40% mark since the 1940s, when hydropower contributed around that percentage and coal made up 55%.
Renewable power sources collectively added a record 858TWh of generation last year – a 49% increase on the previous record set in 2022 of 577TWh.
Solar dominated electricity generation growth for the third year in a row in 2024, adding 474TWh of generation, as shown on the chart below. This was up 29% on 2023.
-
10-04-2025, 11:41 AM #773
SEC begins work on 119MW solar-plus-storage site in Australia
Victoria’s SEC begins construction on 119MW state-owned solar-plus-storage site in Australia
The State Electricity Commission (SEC), a state-owned energy company in Victoria, Australia, has confirmed that construction has started on the 119MW SEC Renewable Energy Park.
The project, which will see a 100MW/200MWh battery energy storage system (BESS) co-located with a 119MW solar PV power plant, will be built in two stages with the support of developer OX2.
As reported previously by Energy-Storage.news, energy storage system integrator Energy Vault will supply the BESS. The system will be built using the company’s X-Vault integration platform and its UL9540 and AS3000-certified B-VAULT integrated BESS enclosures.
Energy Vault, which also provides a proprietary gravity energy storage technology, has been employed by several developers for energy storage sites in Australia. This includes Acen Australia, which confirmed that Energy Vault would provide a 400MWh BESS for the New England project in New South Wales.
Speaking previously on the SEC Renewable Energy Park, Energy Vault’s chairman and CEO, Robert Piconi, said the partnership is “well-aligned” with the company’s mission to accelerate the clean energy transition.
The SEC Renewable Energy Park will be Victoria’s first 100% publicly owned utility-scale renewable energy project. It is estimated to cost around AU$370 million (US$240 million) to develop fully and is being constructed around 300km northwest of the state capital, Melbourne, in Horsham.
In a LinkedIn post, the SEC confirmed that work has started on installing the solar PV, with pre-construction having commenced in February. The site is expected to be fully operational in 2027.
Enough to power 51,000 homes: WATCH: $370m SEC solar project starts construction - Ecogeneration
-
11-04-2025, 04:35 PM #774
California just debunked a big myth about renewable energy
The state went a record 98 of 116 days providing up to 10 hours of electricity with renewables alone.
One of the biggest myths about renewable energy is that it isn’t reliable. Sure, the sun sets every night and winds calm down, putting solar panels and turbines to sleep. But when those renewables are humming, they’re providing the grid with electricity and charging banks of batteries, which then supply power at night.
A new study in the journal Renewable Energy that looked at California’s deployment of renewable power highlights just how reliable the future of energy might be. It found that last year, from late winter to early summer, renewables fulfilled 100 percent of the state’s electricity demand for up to 10 hours on 98 of 116 days, a record for California. Not only were there no blackouts during that time, thanks in part to backup battery power, but at their peak the renewables provided up to 162 percent of the grid’s needs — adding extra electricity California could export to neighboring states or use to fill batteries.
“This study really finds that we can keep the grid stable with more and more renewables,” said Mark Z. Jacobson, a civil and environmental engineer at Stanford University and lead author of the new paper. “Every major renewable — geothermal, hydro, wind, solar in particular, even offshore wind — is lower cost than fossil fuels” on average, globally.
-
16-04-2025, 09:36 AM #775
India reached 220 GW of new renewable energy capacity in 2024-2025
The Indian Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) has announced that the country added 29.52 GW of renewable energy capacity during the 2024-2025 financial year. Solar represented the highest increase with 24 GW of new solar capacity, bringing to a total of 106 GW, which includes 81 GW from ground-mounted projects, 17 GW from rooftop solar systems, 2.9 GW from hybrid projects, and 4.7 GW from off-grid systems. Wind capacity saw an increase of 4.15 GW (up from 3 GW in FY 2023–24), bringing its total installed capacity to 50 GW. Biomass increased by almost 12 GW (including 0.53 GW from off-grid and waste-to-energy sources), and small hydro grew by 5.1 GW with a 440 MW pipeline currently under implementation.
The country’s renewable energy pipeline is estimated to have over 169 GW of renewable energy projects under implementation and 65 GW already tendered. Among the projects, there are about 65 GW of new technologies like hybrid energy systems, round-the-clock power, peaking power, and thermal plus renewable energy bundling.
India targets to reach 500 GW of non-fossil fuel-based energy capacity by 2030.
Thread Information
Users Browsing this Thread
There are currently 1 users browsing this thread. (0 members and 1 guests)



 Reply With Quote
Reply With Quote