Quite interesting. I have not looked into supercapacitors yet. But I have heard Elon Musk, founder of Tesla and SpaceX mentioning them several times. He believes they have high potential.Researchers have developed lightweight "supercapacitors" that can be combined with regular batteries to dramatically boost the power of an electric car.
At the start of his carreer he was offered a post in a supercapacitor research team but decided to start Paypal instead, becoming a self made Billionaire later.
Results 176 to 200 of 731
Thread: Fossil Fuel Alternatives
-
14-11-2014, 04:54 AM #176Thailand Expat
































- Join Date
- Nov 2008
- Last Online
- Yesterday @ 06:02 PM
- Location
- Berlin Germany
- Posts
- 7,069
"don't attribute to malice what can be adequately explained by incompetence"
-
14-11-2014, 04:59 AM #177
They should ban these solar cells as they will cause electricty to be almost free eventually.
first off you will get everyone having heating or Ac on all year round .
Companies will desalinate seawater and irrigate huge desserts, causing massive upheavals in nature the weather / climate, a surge in the earths population and all the extra polution.
All the fake scare stories that you alarmists are claiming for today and co2 will then come true .
-
14-11-2014, 07:20 AM #178
The Netherlands Unveils the World's First Solar Bike Path

The Netherlands has an international reputation as a bike-friendly nation; it’s home to some 18 million bicycles and 21,748 miles of bike lanes. Now, an innovative project—SolaRoad—aims to make even greater use of all that green infrastructure by paving the bike paths with solar cells. On November 12, 2014, the first such path will open: a 70-meter (230 feet) stretch of Krommenie’s bike path will become the first solar-paved right of way in the world
SolaRoad has been in the works since 2009, and is the brainchild of Dutch research institute TNO. The power-generating pavers are created by embedding crystalline silicon solar cells in 8.2 x 11.5 ft concrete slabs, before covering them in a one-centimeter layer of tempered glass. Then, reports the Guardian, a “non-adhesive finish and a slight tilt are [added] to help the rain wash off dirt and thus keep the surface clean, guaranteeing maximum exposure to sunlight.”
These extra steps are pretty important—the flat surface required for transit isn’t exactly ideal for capturing sunlight for power generation. In bike path form the cells are 30 percent less efficient than they would be placed within a standard solar installation. As a result, when this first test strip is extended to its full 100 meters (328 feet) in 2016, it will provide about enough electricity to power three households.
But it does make practical use of an untapped surface area, and there’s plenty of roads available for transformation. Indeed, TNO is not limiting their ambitions to bike paths; the institute estimates that up to 20 percent of the Netherlands’ 140,000km of road could potentially be adapted into SolaRoads, which would amount to an additional 400 to 500 km sq (154 to 193 mi sq) of energy-generating PV which could be fed into the grid, or used to power signage and traffic lights.Keep your friends close and your enemies closer.
-
14-11-2014, 11:44 AM #179Thailand Expat
































- Join Date
- Nov 2008
- Last Online
- Yesterday @ 06:02 PM
- Location
- Berlin Germany
- Posts
- 7,069
Sorry that should read brainfart. Shaking my head in disbelief. Even considering the Netherlands are really densely populated. Originally Posted by S Landreth
Originally Posted by S Landreth
-
29-11-2014, 08:26 AM #180

Quadrofoil is an electric hydrofoiling personal watercraft (PWC), which provides the most economically efficient and completely environmentally friendly mode of recreational marine transportation. Due to hydrofoiling and patented steering technology, riding feels like flying on water and provides an entirely new and thrilling water experience.
The watercraft operates quietly and doesn’t produce any waves or emissions, which makes it suitable for lakes, rivers, seas as well as marine protected areas, where most motor boats and personal watercrafts are prohibited. It has a top speed up to 40 km/h (21 knots) and a range of up to 100 km (54 nautical miles) and can be fully charged in under 2 hours.
Quadrofoil
-
30-11-2014, 06:17 AM #181
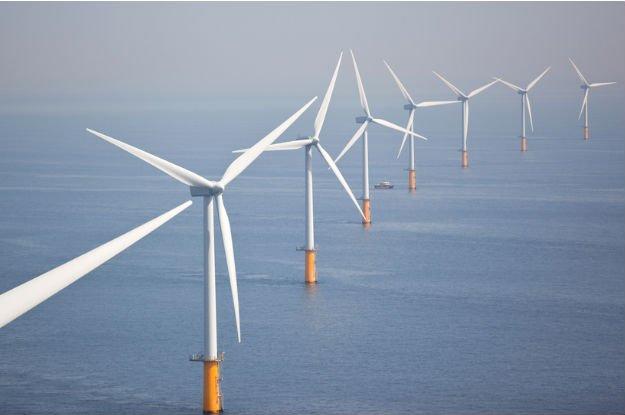

New superconductor-powered wind turbines could hit Australian shores in five years
Australian scientists are developing wind turbines that are one-third the price and 1,000 times more efficient than anything currently on the market to install along the country's windy and abundant coast.
New superconductor-powered wind turbines could be installed off the coast of Australia within the next five years to finally take advantage of the country’s 35,000 km of coastline, which offers up some of the best wind resources in the world.
Developed by a team at the Institute for Superconducting and Electronic Materials at the University of Wollongong in New South Wales, the wind turbines are a significant improvement on current technology. Right now, wind turbines cost about $15 million each to construct, and are super-heavy and tough to ship. They also require a whole lot of maintenance because they're run using a complex, heavy, and costly piece of machinery called a gear box.
“In our design there is no gear box, which right away reduces the size and weight by 40 percent,” said lead researcher and materials scientist Shahriar Hossain. “We are developing a magnesium diboride superconducting coil to replace the gear box. This will capture the wind energy and convert it into electricity without any power loss, and will reduce manufacturing and maintenance costs by two thirds.”
Superconductors are a class of materials that have been getting a lot of attention this year due to their potential to completely revolutionise power systems and batteries as we know them. Right now, these systems generate power by running an electric current through a copper conduction loop, but during this process up to 10 percent of the energy is lost due to resistance. This, and the fact that the copper wire decays quickly, means our current power systems are relatively inefficient with short lifespans.
But superconducting materials generate no electrical resistance, which means they're able to store electricity with no loss of energy. The current is also able to circulate over and over indefinitely, even if power is turned off. The Australian team is making their superconducting coil out of magnesium and boron, both of which are cheap, durable and easy to make.
The team estimates that their superconductor wind turbines will cost just $3-5 million each to build, because by next year, the magnesium diboride coil will cost just $1 per metre to manufacture.
“Australia desperately needs sustainable energy sources. Wind is cheap, clean and we can get it on rainy and sunny days,” he said. "And considering Australia has more than 35,000 km of coastline, there is ample room for offshore wind farms. With industry support, we could install superconducting offshore wind turbines off the coast of Australia in five years, no problem.”
-
02-12-2014, 11:46 AM #182
World's Largest Solar Farm Goes Online In California | IFLScience

Another giant solar farm has been constructed on desert lands in California, stealing the title of the largest solar plant in the world. The farm, which is called Topaz, recently went online after its final 40-megawatt phase was completed, making it the first 500-plus megawatt solar plant to be up and running in the US.
Located in San Luis Obispo County on California’s Carrizo Plain, Topaz consists of a whopping nine million solar panels sprawling across 9.5 square miles of land. This sets it apart from the Ivanpah Solar Power Facility in California’s Mojave Desert, which creates energy by directing sunlight towards a central boiler using thousands of mirrors. While it generates a lot of green energy, the Ivanpah farm has received a lot of criticism because the intense sunlight has been scorching wildlife, in particular birds. Topaz, however, does not use mirrors but photovoltaic solar panels instead.
Construction of the $2.5 billion project began two years ago, but it wasn’t anticipated to be finished until early next year. The company behind the project, First Solar, said that the plant should generate 550 megawatts, which is enough to supply around 160,000 average homes. What’s more, it will also remove 377,000 tons of carbon dioxide each year.
Topaz’s location was chosen after proximity to existing electrical transmission lines, land use and environmental sensitivities were all taken into consideration. According to First Solar, the farm is located on “disturbed farm land” with limited productivity, miles away from the more sensitive areas in the Carrizo Plain National Monument.
Topaz might hold the title for the world’s largest solar farm at the moment, but it will be overtaken possibily as early as next year when the Solar Star plant achieves full capacity, which should generate almost 580 megawatts. Both Solar Star and Topaz are owned by MidAmerican Solar.
-
03-12-2014, 02:28 AM #183Thailand Expat
































- Join Date
- Nov 2008
- Last Online
- Yesterday @ 06:02 PM
- Location
- Berlin Germany
- Posts
- 7,069
This is a way forward if it can be combined with some way of storing energy. In the meantime it has at least the advantage that it will produce most of its energy when aircons need it. Originally Posted by S Landreth
Originally Posted by S Landreth
-
23-12-2014, 07:41 AM #184
MeyGen

The world’s largest tidal energy project, capable of powering nearly 175,000 homes in the U.K. with 400 megawatts of power, will break ground next month in northeast Scotland. Atlantis, majority owner of the MeyGen project, announced that its flagship project had met all the conditions required to start drawing down finance through the U.K.’s Renewable Energy Investment Fund.
The completed project will have 269 sunken turbines, according to Atlantis, which expects to have about 60 of these installed and delivering power by 2020.
In the announcement to investors, Atlantis said: “The major construction and supply contractors to this iconic project have commenced design, engineering and procurement works in readiness for commencement of onshore construction at the project site in Caithness in January 2015.”
Tim Cornelius, Chief Executive Officer of Atlantis, said that Lockheed Martin’s project-specific 1.5 megawatt turbines were scheduled to be delivered on time for construction purposes. In November, the MeyGen project was awarded the first-ever Navigator Award at the International Conference on Ocean Energy, in recognition of the “project’s significant contribution to global marine renewable industry.”
Scotland is trying hard to harness all forms of renewable energy as part of its goal of generating 100 percent of its electricity demand from renewables by 2020. The wind-rich country is home to around a quarter of Europe’s total offshore wind capacity. In October, the Scottish Government approved four huge new offshore wind farms that could produce more than 2.2 gigawatts of power, enough to power 1.4 million homes.

-
29-12-2014, 06:11 AM #185
A Zero-Emissions House That Charges Itself and Your Electric Car Too

Architecture firm Snøhetta has put its stamp on some pretty high profile places, with some very high profile projects: The Oslo Opera House, of course, and the National September 11 Memorial Museum Pavilion in New York City. Soon enough, their overhaul of Times Square will cater to the 400,000-plus pedestrians that walk through the site every day.
The firm, which has main offices in Oslo, Norway, and New York City, works on some quieter projects too, like this ZEB Pilot House, situated in a less-than-glamorous industrial stretch of Larvik, Norway, some 80 miles south of Oslo. Even though it’s out of the limelight, the ZEB house—a collaboration between Snøhetta and the Research Center on Zero Emission Buildings—could have a major impact on residential architecture going forward: Not only is it a zero emissions house, it’s a “plus house,” meaning it actually produces excess energy. It’s enough that an electric car could drive for 12,500 miles on the surplus energy from the ZEB.

Most of this happens through the solar panel roof, which is tilted at at 19-degree angle towards the southeast, to capture as much light as possible. A 45-degree angle would have actually been the optimum position, said lead architect Anne Cecilie Haug, but that would have made the house cartoonish in scale and difficult to build. Settling on the best angle for capturing light over a long period of time “took all this back and forth with the engineers and us,” she says. But the tilted roof can be modified and applied to other buildings in new orientations. A home in Australia, for instance, would need to tilt north. And buildings with different functions might want to capitalize on certain times of day. “An office building would want to harvest more electricity in the middle of the day when everyone’s running their computers,” Haug says of a building that might want a flatter angle, to catch noon light.
Because solar energy is most efficient when used in real time (when panels are harvesting electricity), the ZEB house is especially enabled by connected home gadgets. Using a smartphone to turn on the washing machine while you’re at work means the house can power itself off available daylight, rather than stored energy. Or smart thermostats (with the help of geothermal heating and a heat exchange system connected to the home’s gray water recycling) can remember to conserve electricity for Friday nights, to optimize heating when families are home.
Tricked out as it is, the ZEB Pilot House is ultimately designed for people, so Snøhetta was careful to include a series of organic, but still energy-saving touches, like beeswax-laminated aspen wood in the bedrooms. The wax reacts with natural moisture in the air, helping to keep the room temperature steady. The concrete and bricks supporting the solar roof came from the “Norwegian version of eBay” and can naturally trap heat and cool air, conserving some energy from the house’s heating and cooling system. “We tried to make an outdoor and indoor situation which felt like real home,” Haug says. “It’s a very high tech house, but we were working a lot to make it feel homey, make it feel like somewhere you can live.”
-
06-01-2015, 08:36 AM #186
Scotland could be fossil fuel-free by 2030, says report | Environment | The Guardian

A fossil fuel-free Scotland is not only technically achievable but could prove a cheaper and safer option than pursuing fossil fuel-based development, according to a new WWF-backed report.
The study by consultancy giant DNV-GL tested the viability of the Scottish government’s current policy goal of decarbonising the country’s electricity generation by 2030, setting a target of bringing carbon intensity down from 271 grams of CO2 per kilowatt hour to 50g CO2/kwh.
The target is separate to the goal of providing 100% of electricity demand from renewables by 2020, which still allows for coal and gas to remain on the grid.
The 2030 decarbonisation policy assumes carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology will be operating at scale, fitted to 2.5GW of gas power plants. WWF deems this a risky strategy considering there are no commercial-scale CCS operations in the UK and the government has yet to decide a winner for its £1bn commercialisation competition for the technology between the Peterhead CCS project and the White Rose project at Drax.
However, the report says CCS is not needed to decarbonise Scotland’s electricity sector and concludes “a renewables-based, efficient, flexible, electricity system is perfectly feasible by 2030” given Scotland’s abundance of wind and wave energy resources and strong tradition of engineering innovation.
While electricity production accounts for around a third of Scotland’s emissions, renewables are already the country’s biggest electricity generator - outstripping nuclear, coal and gas - and in November wind turbines alone produced more than 100% of the country’s domestic electricity needs.
-
08-01-2015, 09:11 AM #187
Denmark Sets World Record For Wind Power Production

Denmark has been long been a pioneer in wind power, having installed its first turbines in the mid-1970s when oil shocks sent the import-dependent nation on a quest for energy security. Thirty-seven years later, the country has set a new world record for wind production by getting 39.1 percent of its overall electricity from wind in 2014. This puts the Northern European nation well on track to meet its 2020 goal of getting 50 percent of its power from renewables.
-
11-01-2015, 06:36 AM #188
New Wind Turbine That Looks Like A Tree Is Coming To Paris

One of the biggest criticisms against wind turbines is that they aren’t usually nice to look at, but that may be about to change thanks to the French company NewWind. Their new device, Tree Vent, is an array of vertical wind turbines that look a lot like a tree.
Though the tree looks like a piece of modern art that would fit in at any urban area, it also provides a very important function. Each tree has a current power output of 3.1 kilowatts, which might not be able to power much on its own. However, using several of the trees together as landscape features in a park or along a roadside would make more of an impact to the homes and buildings nearby.
The trees are 11 meters (36 ft) tall, and 8 meters (26 ft) in diameter at its widest point, which makes it about the same height as many urban trees. The white frame of the tree is made out of steel, and it can hold 72 turbines that sit vertically. This orientation cancels out noise, allowing the turbine to spin silently. Wind turbines are typically very tall in order to reach the altitude where the wind is stronger, but these vertical turbines are able to spin with wind blowing as low as 7 km/h (4.4 mph), making this twice as sensitive as traditional turbines. However, they are durable enough to withstand Category 3 winds, which can reach 178 - 208 km/h (111-129 mph).
Click on the top of the video to open and watch it
-
14-01-2015, 06:02 AM #189
Low carbon battery-powered train carries first passengers
Five-week trial will see first battery locomotive operating on the UK rail network in more than 50 years
A new battery-powered train will pick up its first passengers this week, signalling that the days of noisy and polluting diesel engines may soon be a thing of the past.
Following successful trials of a prototype at test tracks in Derby and Leicestershire last year, the modified Class 379 Electrostar battery-powered train – also known as an Independently Powered Electric Multiple Unit (IPEMU) – will run a weekday service for five weeks between Harwich International and Manningtree stations in Essex.
The IPEMU, which has been emblazoned with ‘Batteries Included’ livery, is the first battery-powered train to run on the UK’s rail network in more than half a century.
National Rail said it will contribute to the company’s goal of reducing its environmental impact, improving sustainability and reducing the cost of running the railway by 20% over the next five years.
Should the trial prove successful, a fleet of battery-powered trains could be seen across the network, potentially providing a cost-effective and zero emission replacement for the diesel engines that are still commonly used on branch lines.
“We are always looking for ways to reduce the cost of running the railway and make it greener too,” said Network Rail principal engineer James Ambrose. “This project has the potential to contribute significantly towards both those goals.”
Battery locomotives have actually been around for a century, although they have rarely been used to carry passengers. Munitions factories during world war one used battery power to avoid the risk of explosion from sparks emitted by steam locomotives, while London Underground currently has a fleet of battery locomotives used on engineering trains when the power is switched off for track maintenance and improvement work.
-
15-01-2015, 04:40 AM #190
Every 2½ Minutes, A New Solar Power System Is Connected (US)

GTM Research has released an interesting new statistics regarding solar power in the United States… Ah, yes, you’ve already noticed it in the title above. As it says, a solar PV system is indeed installed in the USA every 2½ minutes, on average.
Putting this into a bit of context, Stephen Lacey notes that “Ten years ago, a system was going up every two hours on average.”
That’s also up from every 4 minutes in 2013, a statistic that even President Obama has mentioned (in 2014’s State of the Union address). Of course, the most systems were installed on homes. Approximately 200,000 solar PV systems were installed in the residential market. It wasn’t stated how many were installed in other sectors of the solar market, but the straight math just leaves about ~10,000 more. Again, that’s not at all surprising, and it’s really the residential solar number that interests most of us.
________________
U.S. Solar Firm Commits $4 Billion And 5 Gigawatts Of Solar In Major Deals With India

India is a country of big numbers. Nearly 1.3 billion people; more than 400 million of them don’t have electricity. Narendra Modi, India’s recently elected populist prime minister, has made providing power, even if just one lightbulb’s worth, to these wanting citizens during his term a priority. While Modi is pursuing all avenues of power creation — India’s coal union went on strike last week to protest opening the sector to international firms — he has been an outspoken advocate of renewable energy, especially solar. In the last decade India’s renewable energy capacity has gone from just under 4 gigawatts to over 27 gigawatts, much of it wind or hydro. The country has a goal of installing 10 gigawatts of solar by 2017 and 20 by 2022.
On Monday, the country took another stride toward these goals through two deals with the large U.S.-based solar company SunEdison. In dual announcements, SunEdison revealed that it signed two memorandums of understanding with India: to develop five gigawatts of renewable energy within five years in the southern Indian state of Karnataka and to build a $4 billion solar manufacturing facility as a joint venture with Adani Enterprises, a large Indian power operator. According to the press release, it will be the largest manufacturing facility of its kind in India, with an annual production capacity of 7.5 gigawatts.
“This facility will create ultra-low cost solar panels that will enable us to produce electricity so cost effectively it can compete head to head, unsubsidized and without incentives, with fossil fuels,” said Ahmad Chatila, President and Chief Executive Officer of SunEdison, in a statement.
The facility, which will create 4,500 direct jobs and over 15,000 indirect jobs, will be based in the north Indian state of Gujarat. Before becoming prime minister, Modi was Chief Minister of Gujarat where he helped grow the state’s nascent solar industry. Now as prime minister, Modi has turned his eye to the country’s overall solar industry, saying that he wants foreign companies to lead investment of over $100 billion to help push India’s solar energy capacity to 100 gigawatts, some 33 times what it is now. SunEdison and other major international solar firms are being drawn in by Modi’s enthusiasm and the country’s overall potential.
-
30-01-2015, 06:58 AM #191
Bangladesh aims to be world’s 'first solar nation'

DHAKA, Bangladesh (Thomson Reuters Foundation) - Residents of Islampur, a remote village in the northern Bangladeshi district of Naogaon, were stunned one night last summer when the darkness was suddenly illuminated by electric lights coming from a village home.
Why the surprise? The community has no connection to the country’s power grid.
Snip
According to the government-owned Infrastructure Development Company Limited (IDCOL), which began the solar home system project in 2003, 3.5 million households – about 10 percent of the country’s total – had installed SHS by the end of 2014.
"Every month, 50,000-60,000 Bangladeshi households are connected with a solar home system. In May 2014, more than 80,000 connections were made,” said Mahmood Malik, head of IDCOL. The company runs the scheme with 47 partners, including nongovernmental organisations and businesses.
Snip
"My dream is to empower 75 million Bangladeshis through renewable energy by 2020 and make Bangladesh the first comprehensive solar nation of the world,” he said.
The government is providing low-interest loans to private companies to import and install solar panels for SHS, while businesses offer households or end-users low down-payments and the option to repay the cost of a solar home system over a period of one to three years. A 100 watt panel costs around 50,000 Bangladeshi taka ($640).
_____________
New figures released by GTM Research show that the Latin America solar PV market grew by 370% in 2014, installing a total of 625 MW.
Latin America comprises Mexico, Central America, South America, and the Caribbean, a number of regions that have each been making big inroads in renewable energy generation.

he regional Latin America leader was Chile, making up more than three-quarters of the Latin America total. As an example, in the fourth quarter of 2014 alone, Chile installed double the amount of Latin America’s annual solar PV total in 2013.
Mexico and Brazil filled out the top three spots, second and third (respectively).
The Latin America region has regularly been touted as one of the new hot-spots for renewable energy growth — especially solar.
_________________
Not for everyone. But some parts of the design should be considered.
Builders’ New Power Play: Net-Zero Homes
Industry Wants to Bring Electricity-Generating Housing to Mass Market, but Potential Buyers Must Be Sold on Price

Net-zero homes are going mainstream, if the home-building industry has anything to do with it.
The homes, which generate more electricity in a year than they use, have long been viewed as a niche product for the affluent who can afford custom homes. The chief problem is that it is expensive to get a home to net-zero status, and many customers aren’t willing to wait several years for their electricity-bill savings to cover the thousands of dollars they would have to spend on net-zero features such as solar panels and energy-efficient windows, doors and appliances.
But some builders, motivated by what they deem as rising demand from home buyers and state and local regulators, are aiming to change those perceptions by designing such homes for the mass market. Such a model home—the latest in the National Association of Home Builders’ annual New American Home series showcasing new-home designs —is on display this week in a hillside neighborhood 7 miles from the Las Vegas Strip as part of the trade group’s International Builders Show.
The 5,800-square-foot home, designed and built by the trade group and Blue Heron Design/Build LLC, is being shown in a format that will enable other builders to incorporate elements of the design in mass-market homes across the country. The company says it can build similar—but smaller—net-zero electricity homes for about $700,000. Blue Heron anticipates listing the New American Home for $2.5 million.
-
11-02-2015, 08:02 AM #192
One Of The World's Largest Solar Energy Farms Is Now Open In California

The largest solar farm on American federal public land was dedicated on Monday in California’s Riverside County desert, a project the state hopes will help it meet its ambitious renewable energy goals.
The Desert Sunlight Solar Farm — a 550-megawatt farm that is also one of the largest solar plants in the world — began operating in December 2014, but Monday marked the day it was officially dedicated by U.S. Interior Secretary Sally Jewell. Jewell said the project can provide enough energy to power more than 160,000 average California homes every year — a huge help for the state in meeting its goal to increase its renewable electricity use to 50 percent by 2030.
______________
What the net-zero homes of the future will look like?
While previously the purview of a very niche (and often expensive) housing market, net-zero homes are quickly becoming both an economically sound and sustainable proposal. The average price of an installed solar-power systems has declined more than 50% since 2010 and in 42 out of 50 of America’s largest cities, fully-financed, typically-sized solar system costs less that local utility energy. Right now, only 370 homes certified as ‘net-zero energy ready’ by Department of Energy, but demand continues to rise considerably. So what will the future of net-zero living look like?

________________
Porsche Pajun To Be Electric-Only Tesla Competitor?

The Panamera Junior (where the name “Pajun” was derived) was initially going to be offered with gas and diesel engine options, alongside the electric drivetrain. But the latest report indicates the conventional drivetrains are being dropped in favor of a dedicated battery-electric system. The reasoning? Not because it’ll make for a better electric car, or even because Porsche is afraid of Tesla’s emerging share of the luxury sedan market. Rather, according to the report, Porsche executives feel like the luxury sports sedan segment is currently too crowded for another conventional car that doesn’t bring anything different to the table.
-
18-02-2015, 07:13 AM #193
Apple’s New Headquarters Will Be Powered Entirely By The Sun

On Tuesday, Apple CEO Tim Cook announced the company’s plans to build a 130-megawatt solar farm to power its stores and facilities located in California. Speaking at a technology conference hosted by Goldman Sachs, Cook said Apple will work with First Solar to build the $850-million plant, which will be sited on 1,300 acres in the interior of central California’s Monterey County. Apple’s two campuses in Cupertino, several hours’ drive north of the plant, as well as a data center and the state’s 52 Apple stores will all get power from the development, according to Cook.
____________
145 MW Of Offshore Wind Power For Northern Japan
A contract for two offshore wind parks in Japan has been won by Marubeni Corporation. The site is off the coast of Akita Prefecture, in the northern part of Honshu, Japan’s largest island. The 65 MW site is near the Akita port and will have 13 5 MW turbines. An 80 MW park will have 16 5 MW turbines, and will be located near Noshiro port. Both parks should be operating in 2021.

Each of the ports is considered to be a major port for Japan. According to one source, a 1 MW turbine located offshore can power about 400 homes, when there is adequate wind. (Offshore winds tend to blow more consistently, so the number of homes an offshore turbine can provide power to typically is greater than the number of homes that can be powered by land turbines.) If the 1 MW per 400 homes estimate is an accurate figure, the Akita offshore wind farms will provide enough electricity for approximately 58,000 homes.
___________
India Starts Building World’s Largest Solar Plant, Overtaking U.S.
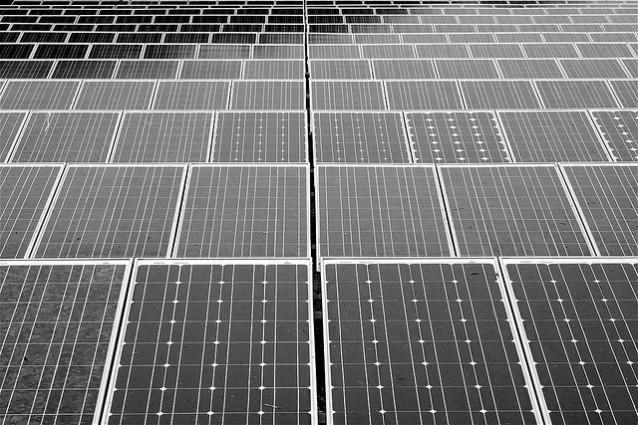

India is about to start construction on what will be the world’s largest solar plant. As part of a redoubled effort to ramp up renewable energy capacity to help meet the developing country’s fast-growing energy needs, the 750-megawatt solar plant in Madhya Pradesh will be inaugurated on August 15, 2016 — India’s Independence Day. The plant will be significantly larger than the world-leading solar farms in California, including the recently-commissioned Desert Sunlight Solar Farm.
Snip
With an average Indian household using only around one-thirteenth of the power required by an average American home, the 750-megawatt project, which will be on 90 percent government-owned land, could bring power to some two million households.
Snip
In one more promising development in India’s quest to increase solar capacity 33-fold in seven years, on Sunday U.S.-based SunEdison and First Solar committed to building more than 20,000 megawatts of clean energy capacity in India by 2022.
_____________
Japan now has more electric car charging points than gas stations
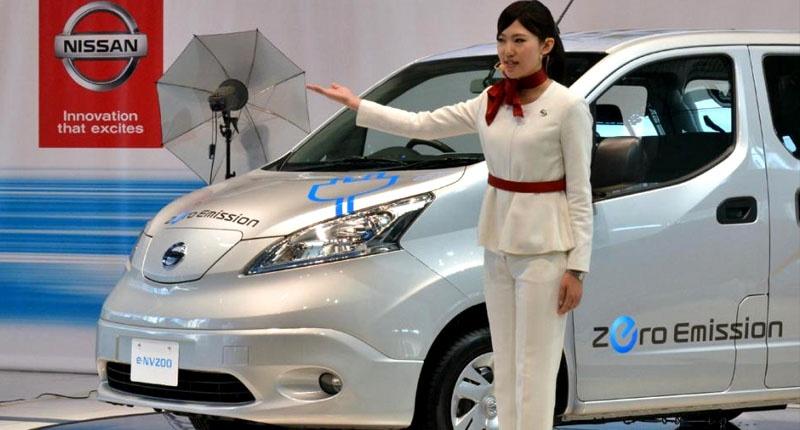

Green-car sceptics take note: Japan now has more electric vehicle charging spots than gas stations.
The country’s number-two automaker Nissan says there are now 40,000 charging units — including those inside private homes — across the nation, compared with 34,000 petrol stations.
While gas stations have multiple pumps and can service many more cars, the figures underscore efforts to boost green-vehicle infrastructure in Japan, long a leader in a sector that remains tiny globally.
-
12-04-2015, 07:35 PM #194
What some countries/cities have done and are going to do,……..
Costa Rica got 100 percent of its electricity from renewables for 75 days straight this year, the state-run Costa Rican Electricity Institute (ICE) announced this week.

The Latin American country hasn’t had to use fossil fuels at all so far in 2015, due to heavy rains that have kept hydroelectric power plants going strong. Wind, solar, biomass, and geothermal energy have also helped power the country this year.
“The year 2015 has been one of electricity totally friendly to the environment for Costa Rica,” ICE announced in a press release in Spanish this week.
This reliance on renewables has prompted the country to lower electricity rates by 12 percent. ICE predicts that rates will continue to drop for Costa Rican customers in the second quarter of the year.
______________
Vancouver commits to run on 100% renewable energy
Canadian city of 600,000 people is the latest to announce it will use only green energy for electricity, transportation, heating and air conditioning within 20 years

Vancouver has become the latest city to commit to running on 100% renewable energy. The city of 600,000 on Canada’s west coast aims to use only green energy sources for electricity, and also for heating and cooling and transportation.
Cities and urban areas are responsible for 70-75% of global CO2 emissions and that’s where “real action on climate will happen” said Park Won-Soon, Mayor of Seoul, South Korea at the ICLEI World Congress 2015, the triennial sustainability summit of local governments where Vancouver made the announcement.
“We are the green tide coming together to save the world from climate change,” Park said to nearly 15,000 members of local government including more than 100 mayors.
Andrea Reimer, Vancouver’s deputy mayor told the Guardian: “There’s a compelling moral imperative but also a fantastic economic case to be a green city.” The 100% goal is likely to be set for a target year of 2030 or 2035.
People and businesses want to live and work in clean and green urban areas, said Reimer, adding that whoever develops expertise in shifting to 100% renewable energy will own the 21st century.
____________
Brazil to Build World’s Largest Floating Solar Farm Amidst Devastating Drought
With Brazil’s historic drought drying up its hydroelectric plants, the South American country is turning to solar power to help relieve its foreboding energy crisis.

The nation announced that within four months, it will commence pilot tests of a gigantic floating solar farm located atop the Balbina hydroelectric plant in the Amazon. It’s currently unclear how physically large the floating farm will be, but the enormous reservoir it will sit on covers 2,360 square kilometers.
At 350 megawatts, Brazil’s ambitious project would easily trump Japan’s currently largest 13.4 megawatt floating solar power plant in terms of power output. To put that in another perspective, the largest solar farm in the world is the 550 megawatt Desert Sunlight Solar Farm in California.
Diversifying energy sources is clearly a necessity for the notoriously parched country. Brazil is experiencing its worst drought in four decades, causing electricity blackouts in many regions. Below-average rainfall in the last few years have depleted its reservoirs, thus gutting its formerly plentiful supply of hydropower, which supplies more than three-quarters of the country’s electricity, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration.
_________________
Spain Got 47 Percent Of Its Electricity From Renewables In March

Spain is getting the vast majority of its electricity from carbon-free sources, the country’s grid operator reported on Tuesday.
According to Red Electrica de Espana (REE), the Spanish peninsula got 69 percent of its electricity generation in March from technologies that produce zero carbon emissions — that is to say, renewable energy plus some of its nuclear power. Nuclear as a whole provided 23.8 percent of the country’s electricity in March, while 47 percent came solely from renewable sources.
Most of the renewable electricity being generated in Spain comes from wind, which alone provided 22.5 percent of the country’s electricity last month. Wind often competes with nuclear for the title of Spain’s top electricity generation source overall — in fact, though nuclear pulled through in March as the top source of electricity, wind has overall provided more electricity to Spain in the entirety of 2015. From January to March, according to REE, wind provided 23.7 percent of electricity generation while nuclear made up 22.7 percent.

Spain has long been a leader in renewable energy, just recently becoming the first country in the world to have relied on wind as its top energy source for an entire year. The country is attempting to use wind power to supply 40 percent of its electricity consumption by 2020, according to CleanTechnica.
______________
US carbon emissions set to fall to lowest level in two decades
Analysts say decline of coal and rise of wind and solar will lead to significant fall in emissions this year, reports RTCC

US efforts to cut greenhouse gas emissions look set for a huge boost this year, with carbon pollution from the power sector set to fall to its lowest level since 1994.
Record numbers of US coal-fired power plants are set to close this year, and analysts at Bloomberg New Energy Finance (BNEF) say this will likely see power sector emissions drop 15.4% below 2005 levels.
Research published today indicates 23GW, 7% of US coal capacity, will come offline due to a combination of low gas prices, new mercury emission standards and the age of closing power plants.
“On an emissions rate basis (t/MWh), 2015 will be the cleanest year in over 60 years for which we have historical data,” says the report.
At the same time investment in renewables is rising fast, with a new 18 gigawatts (GW) of clean energy due to starting feeding into the US grid this year.
BNEF says new solar installations will hit an “all-time high” of 9.1GW, led by California, while new wind build will hit 8.8GW, with a third of new projects in Texas.
-
21-04-2015, 01:09 AM #195
Soon to come,……
Solar power will soon be as cheap as coal

Yada, yada, yada,…….
snip
25 Cents Per Watt
“Getting below $1 [per watt] has exceeded my expectations,” Green says. “But now, I think it can get even lower.”
One likely candidate to get it there is 1366’s new method of wafer fabrication. The silicon wafers behind today’s solar panels are cut from large ingots of polycrystalline silicon. The process is extremely inefficient, turning as much as half of the initial ingot into sawdust. 1366 takes a different approach, melting the silicon in specially built ovens and recasting it into thin wafers for less than half the cost per wafer or a 20 percent drop in the overall cost of a crystalline silicon module. 1366 hopes to begin mass production in 2016, according to van Mierlo.
Meanwhile, thin films, once thought to be the future of solar power, then crushed by low-cost crystalline silicon, could experience a renaissance. The recent record-setting low-cost bid for solar power in Dubai harnesses thin-film cadmium telluride solar modules made by U.S. manufacturer First Solar. The company not only hung on as the vast majority of thin film companies folded, but has consistently produced some of the least expensive modules by increasing the efficiency of their solar cells while scaling up production. The company now says it can manufacture solar modules for less than 40 cents per watt and anticipates further price reductions in coming years.
Ten years from now we could easily see the cost of solar modules dropping to 25 cents per watt, or roughly half their current cost, Green says. To reduce costs beyond that, the conversion efficiency of sunlight into electricity will have to increase substantially. To get there, other semiconducting materials will have to be stacked on top of existing solar cells to convert a wider spectrum of sunlight into electricity.
“If you can stack something on top of a silicon wafer it will be pretty much unbeatable,” Green says.
Green and colleagues set a record for crystalline silicon solar module efficiency at 22.9 percent in 1996 that still holds today. Green doubts the efficiency of crystalline silicon alone will ever get much higher. With cell stacking, however, he says “the sky is the limit.”
A little more,……
A Matter of Size
While solar power is just starting to reach grid parity, wind energy is already there. In 2014, the average worldwide price of onshore wind energy was the same as electricity from natural gas, according to Bloomberg New Energy Finance.

As with solar, the credit goes to technological advances and volume increases. For wind, however, innovation has mainly been a matter of size. From 1981 to 2015 the average length of a wind turbine rotor blade has increased more than sixfold, from 9 meters to 60 meters, as the cost of wind energy has dropped by a factor of 10.
“Increasing the rotor size means you are capturing more energy, and that is the single most import driver in reducing the cost of wind energy,” says D. Todd Griffith of Sandia National Laboratories in Albuquerque, New Mexico.
Griffith recently oversaw the design and testing of several 100-meter-long blade models at Sandia. His group didn’t actually build the blades, but created detailed designs that they subsequently tested in computer models. When the project started in 2009, the biggest blades in commercial operation were 60 meters long. Griffith and his colleagues wanted to see how far they could push the trend of ever-increasing blades before they ran into material limitations.
“I fully expect to see 100 meter blades and beyond.” — D. Todd GriffithTheir first design was an all-fiberglass blade that used a similar shape and materials as those found in relatively smaller commercial blades at the time. The result was a prohibitively heavy 126-ton blade that was so thin and long it would be susceptible to vibration in strong winds and gravitational strain.
The group made two subsequent designs employing stronger, lighter carbon fiber and a blade shape that was flat-backed instead of sharp-edged. The resulting 100-meter blade design was 60 percent lighter than the initial model.
Since the project began in 2009 the largest blades used in commercial offshore wind turbines have grown from 60 meters to roughly 80 meters with larger commercial prototypes now under development. “I fully expect to see 100 meter blades and beyond,” Griffith says.
As blades grow longer, the towers that elevate them are getting taller to catch more consistent, higher speed wind. And as towers grow taller, transportation costs are growing increasingly expensive. To counter the increased costs GE recently debuted a “space frame” tower, a steel lattice tower wrapped in fabric. The new towers use roughly 30 percent less steel than conventional tube towers of the same height and can be delivered entirely in standard-size shipping containers for on-site assembly. The company recently received a $3.7 million grant from the U.S. Department of Energy to develop similar space frame blades.
-
02-05-2015, 01:16 AM #196
Rhode Island’s First Woman Governor Breaks Ground On Nation’s First Offshore Wind Farm

Yesterday certainly was a day of firsts for the great state of Rhode Island, the absolute smallest state in the United States. Governor Gina Raimondo — yes, the first ever woman governor of Rhode Island in like almost 240 years — claimed the offshore wind energy leadership title for her state over the entire US, by officially breaking ground on Block Island, the nation’s very first offshore wind farm.
The Block Island Offshore Wind Farm
Block Island is a 5-turbine, 30-megawatt project of the company Deepwater Wind. It’s actually quite modest, as far as the global offshore wind energy market goes. Scotland, for example, has more than 4 gigawatts (4,000 megawatts) of offshore wind energy in the planning stage on top of several existing projects. An even better example is Denmark, which has already commissioned 1,268 megawatts with plenty more wind energy where that came from.
However, you have to start somewhere. The Block Island project has been in the works since at least 2009, but we only caught wind of it back in 2014, after it cleared several important hurdles.
According to information released by Deepwater last year, the company anticipates 200 local construction, turbine assembly, and cable installation jobs from the new wind farm, on top of dozens of permanent staff and consultants, including environmental assessment professionals such as oceanographers, marine scientists, and biologists.
We were just talking about gigantic, next-generation offshore wind turbines that eschew gearboxes in favor of permanent magnet generators, and as far as we know, that’s what the Block Island farm is getting. Last spring, Deepwater signed an agreement with France’s Alstomfor five Haliade™ turbines, which the company claimed were “the largest turbine installed in offshore waters today.”
The new wind farm is actually just a warmup for a much larger, 1,000 megawatt offshore wind farm that Deepwater has planned for the area, so stay tuned for that.
________________
Everything You Need to Know About Tesla's New Household Batteries

Tesla unveiled a new product line at its design studio in LA tonight. It’s called Tesla Energy and it’s a suite of batteries for homes and for businesses. The existence of the batteries has been one of the worst kept secrets of all time. But we are here at the announcement event and finally have some details. And they’re pretty damn cool.
“Our goal is to fundamentally change the way the world uses energy,” Elon Musk said in a pre-event briefing with the press. “Which sounds crazy.”
It does sound crazy. But that’s the business Musk seems to have gotten himself into.
What are they?
The home battery is called the Powerwall. The business-targeted battery is called the Powerpack. They’re “completely sustainable, zero carbon,” as Musk puts it.
The Powerwall increases the capacity for a house with solar panels, but can also be used during power outages. It can fit on the wall in your garage—to power your Tesla, of course—or the outside wall of your house. It’s about 3 feet across, 4 ft tall, and 6 inches deep. It comes with a 10 year warranty.
It’s connected to the internet so it’s constantly talking to Tesla Energy and monitoring usage.
How much do they cost?
Tesla’s selling price to installers is $3500 for 10kWh and $3000 for 7kWh.
Business battery prices haven’t been made public as of yet.
How do they get installed?
“We’re working with certified installers for the Powerwall,” Musk said. “It’s designed to be easy to install, with two people in maybe a half an hour to an hour.”
When can I get one?
You can order the Tesla Powerwall battery now online but they’re not slated for release until late summer. The Powerpack (business version) will start to become available later this year. They’ll be making a larger push with businesses in 2016.
But that being said, they’re already out in the real world. The company partnered with SolarCity for a pilot project in California that supplied roughly 300 homes with the batteries. About a dozen Walmart stores in California and a Cargill animal processing plant have the business-grade batteries and have been testing those as well.
Tesla Energy plans to be in Germany and Australia by the end of the year. He also sees potential uses in developing countries with little access to reliable power. “In a lot of places there are no utility lines,” Musk said.
What are the specs for the home version?
• Energy: 7kWh or 10kWh
• Continuous Power: 2kW
• Peak Power: 3kW
• Round Trip Efficiency: >92%
• Operating Temperature Range: -20C (-4F) to 43C (110F)
• Dimensions: H: 1300mm W: 860mm D:180mm
Should I buy one?
Well, that depends on a lot of things. Do you have a home? Do you live in an area with a lot of sunlight? Do you have a bunch of extra cash to make an investment in clean energy? Then yes, you should definitely look into the Tesla Energy line of products.
Do they come in different colors?
They certainly do.

-
02-05-2015, 05:06 AM #197Thailand Expat
































- Join Date
- Nov 2008
- Last Online
- Yesterday @ 06:02 PM
- Location
- Berlin Germany
- Posts
- 7,069
Yes it does. But this is Elon Musk. He has never started anything, that did not sound totally crazy. Originally Posted by S Landreth
Originally Posted by S Landreth
He is estimated at 12 Billion $ at the moment, fast rising. Right now he is building a Mega-Factory, the largest factory in the world for this kind of batteries. And it is only the first out of a series he is planning. He expects the battery business of Tesla alone to become a multi Billion $ per year business. Storage of regenerative energy is the missing cornerstone of reusable energy and he believes this will be it.
Of course he is also building a Giga-Factory for solar panels. Producing a gigawatt capacity of panels per year. Which is supposed to be only the first of a series of factories.
-
12-05-2015, 02:36 AM #198
Hawaii Aims for 100 Percent Renewable Power by 2045
To reduce oil imports, Hawaii may become the first state to attempt to eliminate fossil fuels

Hawaii is on the verge of being the first state in the U.S. to set a goal of generating all of its electricity from renewable energy sources.
Under a bill the Hawaii Legislature passed this week, 100 percent of the state’s electricity would be generated with renewables by 2045. If Gov. David Ige approves the measure—he has until the end of June to sign it—it will put the state’s climate goals far ahead any other, and extend Hawaii’s Clean Energy Initiative through mid-century. The initiative aims to reduce the state’s dependency on oil, which generates most of its electric power.
Hawaii has more than climate change in mind in completely converting to renewables. The state’s goal, according to the bill, is to stop importing fuel. The state imports about 93 percent of all its energy, making its residential electric power rates among the most expensive in the nation—about 175 percent of the U.S. average. Already, the state gets about 22 percent of its electricity from renewables, mostly from wind and solar.
__________________
The World’s First Solar Road Is Producing More Energy Than Expected
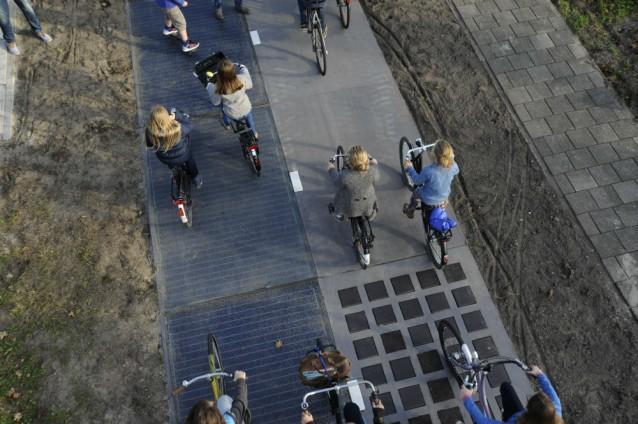

In its first six months of existence, the world’s first solar road is performing even better than developers thought.
The road, which opened in the Netherlands in November of last year, has produced more than 3,000 kilowatt-hours of energy — enough to power a single household for one year, according to Al-Jazeera America.
“If we translate this to an annual yield, we expect more than the 70kwh per square meter per year,” Sten de Wit, a spokesman for the project — dubbed SolaRoad — told Al Jazeera America. “We predicted [this] as an upper limit in the laboratory stage. We can therefore conclude that it was a successful first half year.”
De Wit said in a statement that he didn’t “expect a yield as high as this so quickly.”
The 230-foot stretch of road, which is embedded with solar cells that are protected by two layers of safety glass, is built for bike traffic, a use that reflects the road’s environmentally-friendly message and the cycling-heavy culture of the Netherlands. However, the road could withstand heavier traffic if needed, according to one of the project’s developers.
So far, about 150,000 cyclists have ridden over the road. Arian de Bondt, director of Ooms Civiel, one of the companies working on the project, said that the developers were working on developing solar panels that could withstand large buses and vehicles.
__________________
If you haven’t seen it, you might want to watch.
-
21-05-2015, 02:32 AM #199
Wales launches £25m underwater kite-turbine scheme
Anglesey renewable energy project to generate enough electricity to power 8,000 homes

A unique renewable energy scheme involving underwater “kite-turbines” is being launched off the coast of north Wales.
As part of the £25m project, 20 turbines will be anchored off Anglesey and when fully operational should generate enough electricity to power 8,000 homes.
Initially 30 jobs will be created but if the system works well, the Swedish company behind it, Minesto, believes hundreds more could follow.

___________
France decrees new rooftops must be covered in plants or solar panels
All new buildings in commercial zones across the country must comply with new environmental legislation

Rooftops on new buildings built in commercial zones in France must either be partially covered in plants or solar panels, under a law approved on Thursday.
Green roofs have an isolating effect, helping reduce the amount of energy needed to heat a building in winter and cool it in summer.
They also retain rainwater, thus helping reduce problems with runoff, while favouring biodiversity and giving birds a place to nest in the urban jungle, ecologists say.
The law approved by parliament was more limited in scope than initial calls by French environmental activists to make green roofs that cover the entire surface mandatory on all new buildings.
_____________
Work to begin next year on first windfarm off England's south coast
The 400-megawatt Rampion windfarm eight miles from Sussex coast could power up to 300,000 homes at a cost of £1.3bn

Construction of the first windfarm off the south coast of England will begin early next year, it has been announced.
The 400-megawatt Rampion windfarm, situated eight miles from the Sussex coast, could power up to 300,000 homes and will cost £1.3bn.
Up to 450 jobs could be created during the main building phase of the Rampion project, which consists of 116 turbines and could cut CO2 emissions by up to 600,000 tonnes a year.
Amber Rudd, the energy secretary, said: “This huge investment is a vote of confidence in the UK, creating local jobs, bringing business opportunities and providing clean, homegrown energy.”
E.ON said onshore construction of the substation at Twineham, West Sussex, will start next month, followed by preparations for the onshore cable route. The energy company said offshore construction was expected to be completed by 2018.
-
03-06-2015, 02:18 AM #200
some competition for the Tesla powerwall
all this is good , as it will drive innovation and prices
Benz to power houses too - motoring.com.auBenz to power houses too
Daimler follows Tesla lead to charge houses using electric-vehicle technology
The world’s oldest car company has set its sights on becoming the world’s newest household and industrial energy supplier.
While Tesla has stolen the headlines by suggesting it will sell its Model S batteries to help houses store off-peak and renewable electricity, Daimler already has a lithium-ion battery working on Germany’s electricity grid and will go fully commercial in September.
With no German government support for electric vehicles, Daimler has changed tack to help recoup decades of research and plans to offer battery storage set-ups for heavy industry, mid-sized facilities like supermarkets and, soon, households.
Its ACCUmotive subsidiary already has its first large industrial storage setup, with Daimler christening it a “stationary energy storage”, which sounds a lot like the thinking – and practice – behind stationary internal combustion engines.
Daimler founded ACCUmotive in 2009 to develop and sell (even internally) the lithium-ion batteries for plug-in hybrid and electric smarts and Mercedes-Benz models.
Its first stationary energy storage setup is operated by a German electricity joint-venture, Coulomb, to stabilize the Saxony Kamenz power grid by smoothing out the peaks and troughs in power delivery.
It uses 96 lithium-ion modules with more than 500kWh of energy storage, though it plans to expand that to 3000kWh within weeks.
“Mercedes-Benz energy storage systems are the best proof that lithium-ion batteries made in Germany are a model for the future, and not just in cars,” Mercedes-Benz Cars head of electrics/electronic development and E-Drive, Harald Kröger, said.
“With our comprehensive battery knowhow at Deutsche ACCUmotive, we can accelerate the energy revolution both on the road and in the power of businesses and households.
“What we have already proven over millions of kilometres travelled in the most adverse conditions, such as heat and cold and rain and snow, we bring to create the best technology for stationary use.
Daimler and its subsidiaries have been working on repurposing its zero-emissions road-car technologies for industrial and household purposes since 2012, he said.
“We have opened up new growth opportunities with our entry in to the new business field of stationary energy storage for industrial and private clients.”
It already has more industrial plans, including a system for EnBW in retail banking, and is chasing wider distribution around the planet.
“The system developed by Daimler Business Innovation goes far beyond industrial use.
“The operation in mid-trade, such as supermarkets, can also benefit enormously from stationary energy storage by using buffering during consumption peaks, such as on hot days,” he said.
"It is also suitable for private use, so it can be that households can mate it with their own photovoltaic systems, catching the excess solar electricity with virtually no loss.”
It already has test units running for both light industrial, commercial and private use, with private battery modules able to store 2.5kWh and the industrial versions taking 5.9kWh.
“For the private sector, up to eight modules can be combines to give 20kWh of storage, and they can be scaled for commercial and industrial use,” he said.
ACCUmotive has already delivered more than 60,000 lithium-ion batteries and employs more than 250 people near Stuttgart.
Published : Friday, 29 May 2015
Thread Information
Users Browsing this Thread
There are currently 1 users browsing this thread. (0 members and 1 guests)


 Reply With Quote
Reply With Quote




